Flo31
- 1
- 0
- TL;DR
- 3D Heat equation with dirichlet condition in semi infinite domain
Hi,
I am looking for the solution of the following heat conduction problem (see figure below):
I looked into the solutions given by A.V. Liukov Analytical Heat Diffusion Theory (1968), but nothing looks similar to this. The issue, here is the combination of having Dirichlet BC and that the value of temperature on z=0 depends on x and y. Using the properties of door function may help (similarly to the dirac distribution for describing a point source in Green's problem), but I am still not sure how to tackle the problem.
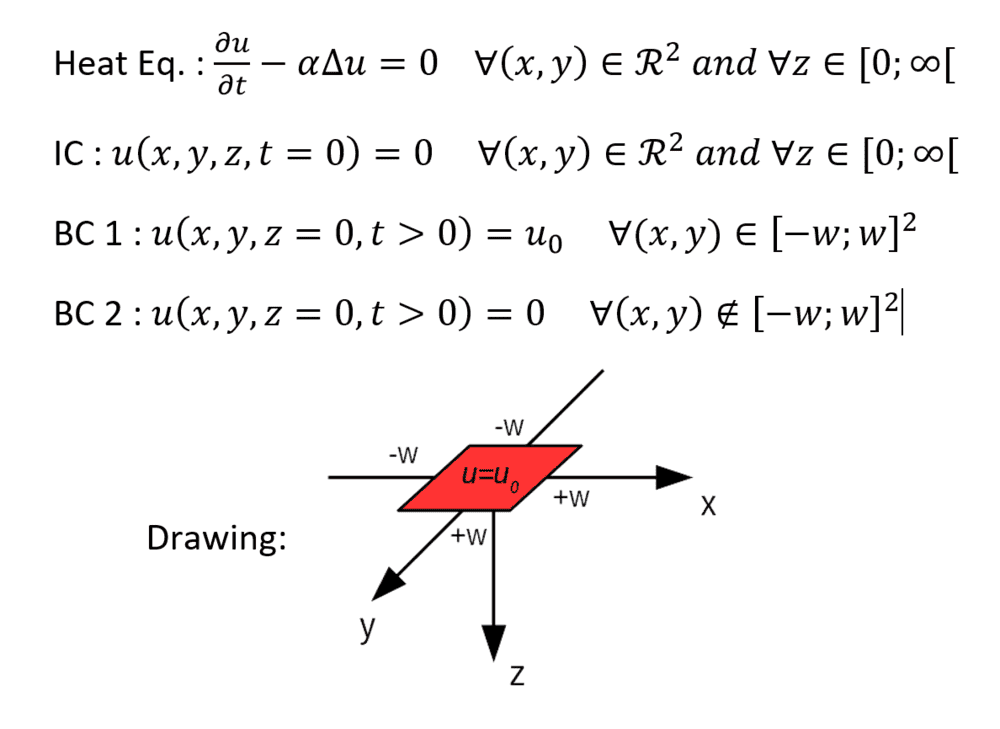 Please let me know your opinion on this problem.
Please let me know your opinion on this problem.
Thanks,
Florian
I am looking for the solution of the following heat conduction problem (see figure below):
- the geometry is the semi-infinite domain such that (x,y)∈R2 and z∈[0,∞[ ;
- the thermal diffusivity is constant;
- the domain is initially at a temperature of 0;
- At t>0, a small square of the surface ((x,y)∈R2) is instantaneously brought at a temperature of u0. The rest of the boundary is maintained at a temperature of 0.
I looked into the solutions given by A.V. Liukov Analytical Heat Diffusion Theory (1968), but nothing looks similar to this. The issue, here is the combination of having Dirichlet BC and that the value of temperature on z=0 depends on x and y. Using the properties of door function may help (similarly to the dirac distribution for describing a point source in Green's problem), but I am still not sure how to tackle the problem.
Thanks,
Florian