Britney2 said:
A. 2 circles that have the same center have their radiuses respectively 5 nd 3 cm. From A which is a point of the big circle are constructet the tangents with the small circles and we mark the pint of tangent A and B. Let's mark D and E the points where these tangents touch the big circle. Find the distance of the center O from DE. (my answer is 1.4 cm but i just don't know if I am right)
B. f(x)= (1-x)^1/2 / x Find the limit when x goes to - infinity.
Thanks in advance!
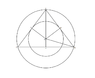
Your problem is not stated very clearly. I'm assuming that you are starting from a point X on the big circle and constructing the 2 tangents to the small circle through point X. (See attached diagram). Then, the tangent points are labeled A and B. The points where the tangent lines cross the large circle are labeled C and D so that you have 2 chords to the big circle, XC and XD, both tangent to the small circle at points A and B, respectively.
If this is correct, I get 1.4cm also:
OX = 5cm since it is a radius to the large circle
OA = 3cm since it is a radius to the small circle
OA must be perpendicular to CX since CX is tangent to the small circle
Also, OB is perpendicular to DX for the same reason
Therefore, triangle OAX makes a right triangle with angle A being the right angle
And triangle OBX is a right triangle with angle B as the right angle
That makes AX = 4cm by Pythagorean theorem
Which means that AC, AX, BD and BX are all equal to 4cm, making CX and DX equal to 8cm
Extend XO until it intersects with CD at a point F
We know that XF must be perpendicular to CD:
triangle OAC = triangle OBD by SAS
Points O and X lie on the perpendicular bisector of CD since they are both equidistant from points C and D
Since F is a point on the extended line through X and O, it bisects CD
Therefore XF is perpendicular to CD
That makes CF = DF
And triangle OFD is a right triangle having right angle F
Now we have
{\overline{XF}}^2 + {\overline{DF}}^2 = {\overline{XD}}^2
and
{\overline{OF}}^2 + {\overline{DF}}^2 = {\overline{DO}}^2
or, rearranging...
{\overline{DF}}^2 = {\overline{DO}}^2 - {\overline{OF}}^2
but since XF = XO + OF, we have
(\overline{XO} + \overline{OF})^2 + {\overline{DF}}^2 = {\overline{XD}}^2
Substituting for DF, we get
(\overline{XO} + \overline{OF})^2 + {\overline{DO}}^2 - {\overline{OF}}^2 = {\overline{XD}}^2
{\overline{XO}}^2 + 2 \cdot \overline{XO} \cdot \overline{OF} + {\overline{OF}}^2 + {\overline{DO}}^2 - {\overline{OF}}^2 = {\overline{XD}}^2
{\overline{XO}}^2 + 2 \cdot \overline{XO} \cdot \overline{OF} + {\overline{DO}}^2 = {\overline{XD}}^2
2 \cdot \overline{XO} \cdot \overline{OF} = {\overline{XD}}^2 - {\overline{XO}}^2 - {\overline{DO}}^2
\overline{OF} = \frac{{\overline{XD}}^2 - {\overline{XO}}^2 - {\overline{DO}}^2}{2 \cdot \overline{XO}}
We know that XD = 8, XO = 5, and DO = 5 so, substituting we get
\overline{OF} = \frac{8^2 - 5^2 - 5^2}{2 \cdot 5} = \frac{64 - 25 - 25}{10} = \frac{14}{10} = 1.4
OF is the perpendicular distance from the center of the circles to line segment CD and it's length is, indeed 1.4cm