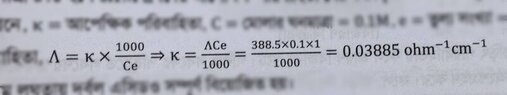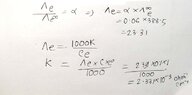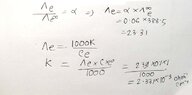Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the conductance of weak electrolytes, specifically addressing different approaches to solving a problem related to their behavior at infinite dilution. Participants are comparing a personal handwritten solution with a reference book's method and noting discrepancies in the use of certain information.
Discussion Character
Main Points Raised
- One participant presents a handwritten solution and references a book that states at infinite dilution, α = 1 (100%).
- Another participant requests clarification on the two approaches, noting the absence of the handwritten attempt in the attached picture.
- Concerns are raised about the reference book's method not utilizing information about a 6% concentration, leading to doubts about its validity.
- Repeated requests for clarification regarding the handwritten solution and the book's note indicate confusion about the presented methods.
- Two participants express agreement with the correctness of the original result presented by the thread starter.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express uncertainty regarding the validity of the reference book's approach, particularly due to its lack of consideration for the 6% information. While some participants agree on the correctness of the handwritten solution, the overall discussion remains unresolved regarding which approach is definitively correct.
Contextual Notes
The discussion highlights limitations in the clarity of the uploaded materials and the assumptions made in both the handwritten solution and the reference book's method. The relevance of the 6% concentration is also questioned but not fully explored.