SUMMARY
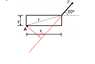
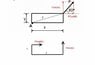
The discussion focuses on calculating the torque exerted by a force F on a rectangular plate at an angle of 60 degrees above the horizontal, specifically about point A, the lower left corner. The correct expression for torque is derived by splitting the force into its x and y components, resulting in the formula: torque = x*F*sin(60) - y*F*cos(60). Participants clarify that the components of force act in opposite directions around point A, necessitating the inclusion of a minus sign in the final torque equation. This understanding resolves the confusion regarding the correct application of torque principles.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of torque and its calculation.
- Knowledge of vector decomposition into components.
- Familiarity with trigonometric functions, specifically sine and cosine.
- Basic principles of mechanics related to forces and moments.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of torque in physics, focusing on the right-hand rule.
- Learn about vector decomposition and how to resolve forces into components.
- Explore the application of trigonometric functions in physics problems.
- Review examples of torque calculations involving multiple forces and angles.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and torque calculations, as well as educators seeking to clarify concepts related to forces and moments.