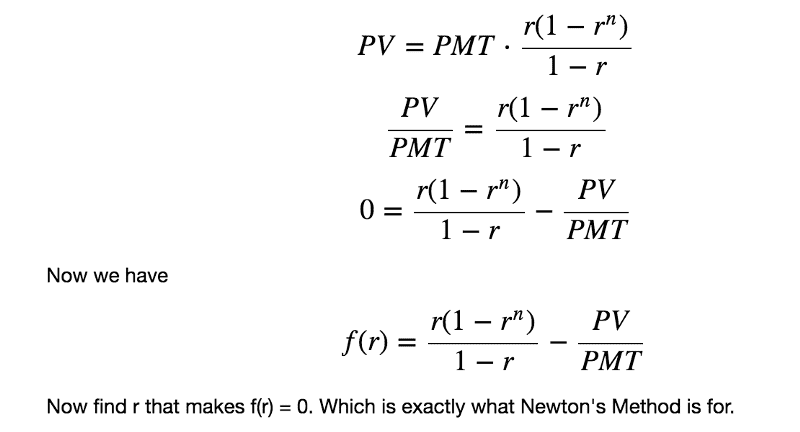Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around solving an algebraic equation related to mortgage payments, specifically focusing on finding the interest rate "r" when it is an exponent in the formula. Participants explore various methods, including algebraic approaches and numerical techniques, while considering the limitations of each method.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant presents an equation for mortgage payments and seeks an algebraic method to solve for "r," questioning whether it can be solved outright.
- Another participant expresses doubt about the existence of an algebraic solution and suggests that Newton's method may be applicable for finding "r."
- A further reply reiterates the applicability of Newton's method and inquires about implementing it in Excel.
- One participant reformulates the original equation into a function suitable for graphing and outlines the steps for applying Newton's method, emphasizing the need for derivatives and iterative calculations.
- Another participant proposes the use of the Excel RATE function, which calculates the interest rate per period of an annuity through iteration, noting that it may not converge in some cases.
- A participant challenges the correctness of the original formula, providing an alternative discount factor for a finite series of payments and suggesting a different approach to calculating present value.
- Another participant introduces the concept of using logarithmic returns and continuous compounding as a way to eliminate exponents in the equation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the best method to solve for "r." There are competing views on the validity of the original formula and the applicability of various methods, including Newton's method and the Excel RATE function.
Contextual Notes
Some participants express uncertainty regarding the algebraic solvability of the equation and the conditions under which numerical methods may fail to converge. The discussion includes various interpretations of the formula and its components, leading to differing approaches to the problem.