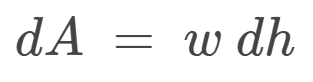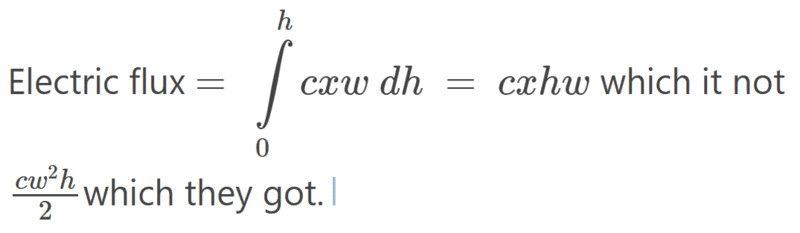Homework Help Overview
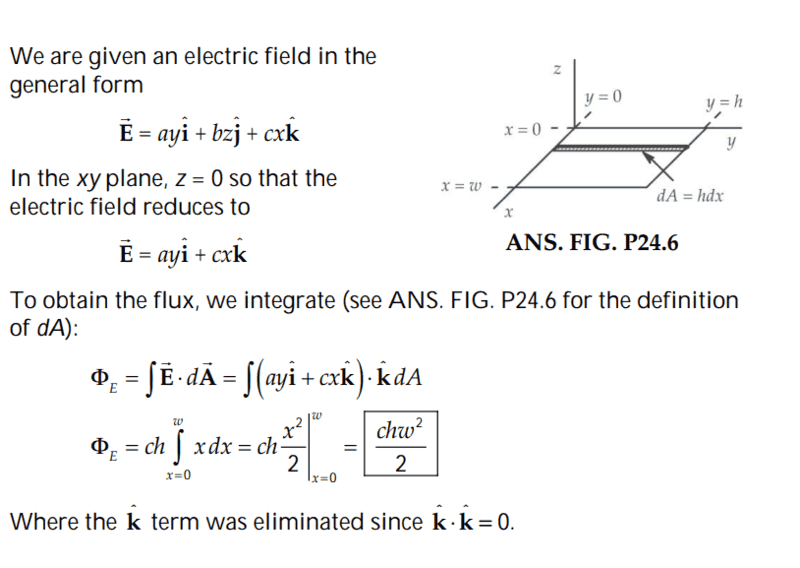
The discussion revolves around finding electric flux in a non-uniform electric field, specifically addressing the integration of differential area elements in the context of double integration.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants explore the correct formulation of differential area for integration, questioning the use of constant versus variable dimensions. There are attempts to clarify the implications of integrating over an area with respect to different variables.
Discussion Status
Participants are actively engaging with the problem, raising questions about the integration process and the assumptions made regarding the electric field components. Some guidance has been offered regarding the treatment of the electric field and the integration method, but no consensus has been reached.
Contextual Notes
Some participants indicate a lack of familiarity with double integration, which may affect their understanding of the problem setup. There are also discussions about the implications of variable dimensions in the context of the electric field.