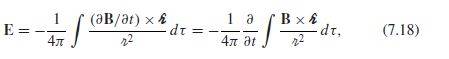SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the derivation of the electric field (E field) analog to the Biot-Savart law, as referenced on page 317 of "INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRODYNAMICS" 4th Edition by Griffiths. Participants suggest using Gauss's law and Maxwell's equations, specifically the identity involving the curl of the electric field, to derive the E field expression. The conversation highlights the relationship between Faraday's Law and Ampère's law, emphasizing the need to adapt the Biot-Savart law for electric fields. Key equations discussed include Gauss's law and the integral forms derived from Maxwell's equations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Maxwell's equations
- Familiarity with Gauss's law
- Knowledge of vector calculus identities
- Experience with electromagnetic theory
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Biot-Savart law from Maxwell's equations
- Learn about the implications of Faraday's Law in electromagnetic induction
- Explore vector calculus identities relevant to electromagnetic fields
- Review the differences between electric and magnetic field equations in electrodynamics
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, electrical engineers, and researchers in electromagnetism seeking to deepen their understanding of the relationship between electric and magnetic fields through mathematical derivations.