Homework Help Overview
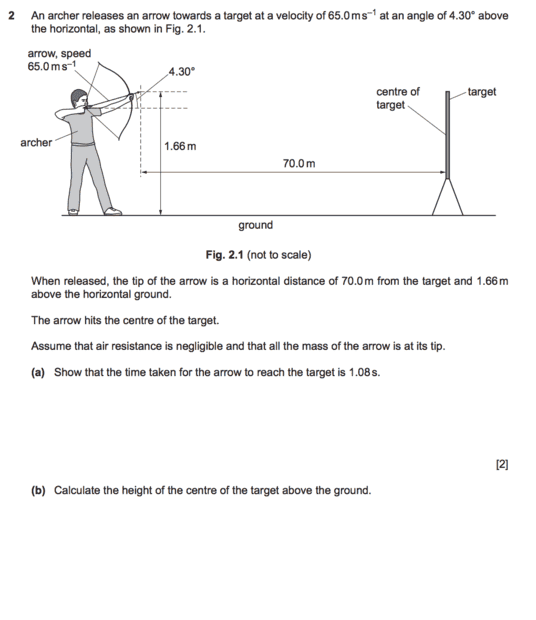
The discussion revolves around the motion of an arrow being fired towards a target, specifically focusing on the acceleration due to gravity and its implications on the arrow's trajectory. The subject area includes kinematics and the application of SUVAT equations.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants explore the use of the SUVAT equations to analyze the motion of the arrow, questioning the sign of the acceleration due to gravity and its consistency throughout the arrow's flight. There is a focus on understanding why acceleration is considered negative when the arrow moves upward initially.
Discussion Status
The discussion is active, with participants seeking clarification on the assumptions regarding the direction of acceleration and the treatment of gravity in the problem. Some guidance has been provided regarding the conventional treatment of upward motion as positive and gravity as negative, though explicit references in the original question are noted as missing.
Contextual Notes
Participants mention that the problem does not explicitly state the direction conventions for positive and negative values, leading to confusion about the treatment of acceleration. The original poster also refers to previous parts of the question for context.