btb4198
- 570
- 10
I am trying to train a model to generate images, I have a dataset of over 17K of men posing. I have been training my model for a few hours now and Sadly all I am getting is this:
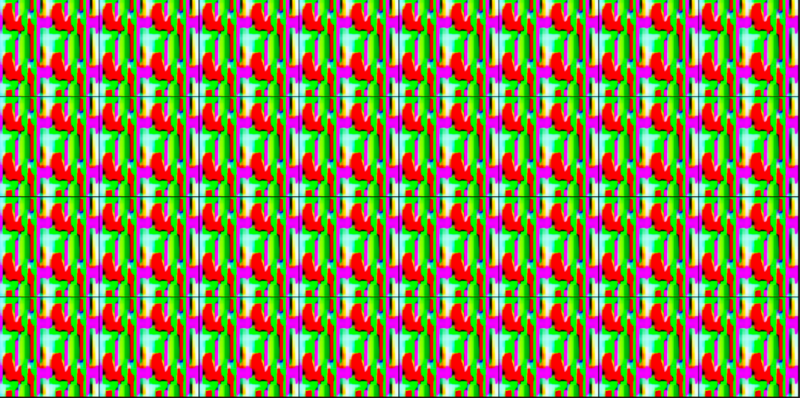
Also my d_loss=-9.79e+3 how is it Negative ?
here is my code:
[CODE title="BigGANModel"]# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""BigGANModel.ipynb
Automatically generated by Colaboratory.
Original file is located at
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1mw6J_dBCCmx6_mwpa7VDHNG7PiR3K2th
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
import urllib.request
from torchvision.transforms import Resize
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torchvision.transforms import ToPILImage
from torchvision import transforms, utils, datasets
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from io import BytesIO
import torchvision.transforms as T
import torchvision.transforms.functional as F
from PIL import Image
from google.colab import drive
from google.colab import files
from tqdm import tqdm
import pickle
import random
import cv2
import os
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
drive.mount('/content/gdrive')
from sys import path
path.append("/content/gdrive/My Drive/Python_Libraries")
import genericgandataset as ggd
from sys import path
path.append("/content/gdrive/My Drive/Python_Libraries")
import reuseablecustompythonfunctions as rcpf
batch_size = 32
num_workers = 4
LEARNING_RATE = 2e-4
betas=(0.5, 0.999)
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
ggd.ImageHeight = 128
ggd.ImageWidth = 128
generator_ImageHeight = 1024
generator_ImageWidth = 1024
val_frequency = 100
evolution_images_per_epoch = 8
val_frequency = 2
LOAD_MODEL = True
SAVE_MODEL = True
CHECKPOINT_DISC = "gdrive/My Drive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Disc_BigGANModel_"
CHECKPOINT_GEN = "gdrive/My Drive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Gen_BigGANModel_"
LOAD_CHECKPOINT_DISC = "/content/gdrive/MyDrive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Disc_BigGANModel_0.pth.tar"
LOAD_CHECKPOINT_GEN = "/content/gdrive/MyDrive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Gen_BigGANModel_0.pth.tar"
evolution_folder ="gdrive/My Drive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/BigGANModelEvolution"
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, upsample=False, downsample=False):
super(ResBlock, self).__init__()
self.upsample = upsample
self.downsample = downsample
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
if upsample or downsample or in_channels != out_channels:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
shortcut_x = self.shortcut(x)
if self.upsample:
out = nn.functional.interpolate(out, scale_factor=2)
shortcut_x = nn.functional.interpolate(shortcut_x, scale_factor=2)
if self.downsample:
out = nn.functional.avg_pool2d(out, 2)
shortcut_x = nn.functional.avg_pool2d(shortcut_x, 2)
out += shortcut_x
return self.relu(out)
class BigGANGenerator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, latent_dim=128):
super(BigGANGenerator, self).__init__()
self.latent_dim = latent_dim
self.proj = nn.Linear(latent_dim, 16 * latent_dim * 4 * 4)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(16 * latent_dim * 4 * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.res_blocks = nn.Sequential(
ResBlock(16 * latent_dim, 8 * latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(8 * latent_dim, 4 * latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(4 * latent_dim, 2 * latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(2 * latent_dim, latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(latent_dim, latent_dim // 2, upsample=True), # Add this layer
ResBlock(latent_dim // 2, latent_dim // 4, upsample=True), # Add this layer
)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(latent_dim // 4, 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = x.view(-1, 16 * self.latent_dim, 4, 4)
x = self.res_blocks(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.tanh(x)
return x
class BigGANDiscriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BigGANDiscriminator, self).__init__()
self.res_blocks = nn.Sequential(
ResBlock(3, 64, downsample=True),
ResBlock(64, 128, downsample=True),
ResBlock(128, 256, downsample=True),
ResBlock(256, 512, downsample=True),
ResBlock(512, 1024, downsample=True),
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.res_blocks(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# Initialize the generator and discriminator objects
generator = BigGANGenerator(latent_dim=128)
discriminator = BigGANDiscriminator()
# Move the generator and discriminator to GPU if available
generator = generator.to(device)
discriminator = discriminator.to(device)
# Set up the optimizers
optimizer_G = optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE , betas=betas)
optimizer_D = optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE , betas=betas)
image_saved_count = 0
g_scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler()
d_scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler()
train_loader = ggd.getdataloaders(batch_size, num_workers)
iterations_per_epoch = ggd.size_of_trainning_dataset // batch_size
evolution_frequency = iterations_per_epoch // evolution_images_per_epoch
if LOAD_MODEL:
rcpf.load_checkpoint(LOAD_CHECKPOINT_GEN, generator, optimizer_G,LEARNING_RATE,)
rcpf.load_checkpoint(LOAD_CHECKPOINT_DISC, discriminator, optimizer_D,LEARNING_RATE,)
def test_discriminator():
ImageHeight, ImageWidth = 128, 128
x = torch.randn((5, 3, ImageHeight, ImageWidth))
test_model = BigGANDiscriminator()
test_model = test_model.to(device)
x = x.to(device)
preds = test_model(x)
print(preds.shape)
test_discriminator()
def test_generator():
# Create a Generator model
test_generator = BigGANGenerator(latent_dim=128)
test_generator = test_generator.to(device)
# Create a random latent vector
z = torch.randn(2, 128).to(device) # or any batch size greater than 1
# Generate an image using the generator
img_generated = test_generator(z)
# Print the generated image shape
print(img_generated.shape)
test_generator()
def test_model(generator, device=device):
generator.eval() # Set the generator to evaluation mode
with torch.no_grad(): # No need to compute gradients for this operation
random_noise = torch.randn(1, 512).to(device) # Create random noise vector
generated_image = generator(random_noise) # Generate image using the generator
# Convert the resized image to a PIL image and display it
image = ToPILImage()(generated_image)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# Define the loss function
def wasserstein_loss(output, target):
return torch.mean(output * target)
def save_images(y_fake, folder, image_saved_count):
save_image(y_fake, f"{folder}/Generated_Image{image_saved_count}.png")
import torch.nn.functional as F
def resize_images(images, size=128):
# Check if the input images have the expected shape
if len(images.shape) != 4:
raise ValueError("Expected input shape: [batch_size, channels, height, width]")
# Rescale the images to the desired size
resized_images = F.interpolate(images, size=(size, size), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
return resized_images
def Test_resize_function(num_images):
toPIL = transforms.ToPILImage()
train_loader = ggd.getdataloaders(num_images, 2) # Set batch size to num_images
for i, test_data in enumerate(train_loader):
# Display the images in a grid
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, num_images, figsize=(20, 2))
for j in range(num_images):
image = test_data[j]
#image = resize_images(image.unsqueeze(0),128)
image = image.squeeze(0)
axs[j].imshow(toPIL(image.cpu()))
axs[j].axis('off')
plt.show()
print(test_data.shape)
break
Test_resize_function(5)
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
def train_BigGAN2(train_loader, epochs, save_file_index):
# Initialize the networks
training_losses = []
validations_losses = []
training_accuracies = []
validation_accuracies = []
global image_saved_count
# Training loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
loop = tqdm(total=len(train_loader), position=0, leave=False)
for i, real_images in enumerate(train_loader):
real_images = real_images.to(device)
batch_size = real_images.size(0)
# Update the discriminator
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
real_labels = Variable(torch.ones(batch_size, 1).to(device))
fake_labels = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, 1).to(device))
# Calculate the discriminator loss for real images
real_output = discriminator(real_images)
real_loss = wasserstein_loss(real_output, real_labels)
# Generate fake images
z = torch.randn(batch_size, 128).to(device)
fake_images = generator(z)
save_image = fake_images
# Calculate the discriminator loss for fake images
fake_output = discriminator(resize_images(fake_images.detach()))
fake_loss = wasserstein_loss(fake_output, fake_labels)
# Calculate the total discriminator loss and update the discriminator
d_loss = torch.mean(fake_loss) - torch.mean(real_loss)
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
# Update the generator
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# Calculate the generator loss
fake_output = discriminator(resize_images(fake_images))
g_loss = wasserstein_loss(fake_output, real_labels)
# Update the generator
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
loop.set_postfix(d_loss=d_loss.item(), g_loss=g_loss.item())
loop.set_description(f"Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{epochs}]") # Update epoch number
loop.update(True) # Refresh the progress bar
if i % evolution_frequency == 0:
save_images(save_image, evolution_folder, image_saved_count)
image_saved_count += 1
if SAVE_MODEL and epoch % 5 == 0:
rcpf.save_checkpoint(generator, optimizer_G , save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_GEN)
rcpf.save_checkpoint(discriminator, optimizer_D, save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_DISC)
save_file_index = save_file_index + 1
loop.close()
return training_losses, training_accuracies
training_accuracies = []
training_losses = []
save_file_index = 0
try:
training_losses, training_accuracies = train_BigGAN2(train_loader, epochs=10000, save_file_index = 1)
except Exception as e :
print(e)
torch.set_printoptions(profile = "default")
import traceback
print(traceback.format_exc())
rcpf.save_checkpoint(generator, optimizer_G , save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_GEN)
rcpf.save_checkpoint(discriminator, optimizer_D, save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_DISC)
# Plotting training losses
fig = plt.figure()
plt.title("Training Losses")
plt.xlabel("Iterations")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.plot(training_losses, label='Training Loss', alpha=.5)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Plotting training and validation accuracies
fig = plt.figure()
plt.title("Training Accuracies")
plt.xlabel("Iterations")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.plot(training_accuracies, label='Training Accuracy', alpha=.5)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
test_model(generator)[/CODE]What did I do wrong ? did I Messed up the wasserstein_loss ?
[CODE title="wasserstein_loss"]def wasserstein_loss(output, target):
return torch.mean(output * target)[/CODE]
why I am getting :
d_loss=-9.95e+3, g_loss=7.18e+3
I started training last night.
Also my d_loss=-9.79e+3 how is it Negative ?
here is my code:
[CODE title="BigGANModel"]# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""BigGANModel.ipynb
Automatically generated by Colaboratory.
Original file is located at
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1mw6J_dBCCmx6_mwpa7VDHNG7PiR3K2th
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
import urllib.request
from torchvision.transforms import Resize
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torchvision.transforms import ToPILImage
from torchvision import transforms, utils, datasets
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from io import BytesIO
import torchvision.transforms as T
import torchvision.transforms.functional as F
from PIL import Image
from google.colab import drive
from google.colab import files
from tqdm import tqdm
import pickle
import random
import cv2
import os
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
drive.mount('/content/gdrive')
from sys import path
path.append("/content/gdrive/My Drive/Python_Libraries")
import genericgandataset as ggd
from sys import path
path.append("/content/gdrive/My Drive/Python_Libraries")
import reuseablecustompythonfunctions as rcpf
batch_size = 32
num_workers = 4
LEARNING_RATE = 2e-4
betas=(0.5, 0.999)
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
ggd.ImageHeight = 128
ggd.ImageWidth = 128
generator_ImageHeight = 1024
generator_ImageWidth = 1024
val_frequency = 100
evolution_images_per_epoch = 8
val_frequency = 2
LOAD_MODEL = True
SAVE_MODEL = True
CHECKPOINT_DISC = "gdrive/My Drive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Disc_BigGANModel_"
CHECKPOINT_GEN = "gdrive/My Drive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Gen_BigGANModel_"
LOAD_CHECKPOINT_DISC = "/content/gdrive/MyDrive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Disc_BigGANModel_0.pth.tar"
LOAD_CHECKPOINT_GEN = "/content/gdrive/MyDrive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/CNN_Models/BigGANModel/Gen_BigGANModel_0.pth.tar"
evolution_folder ="gdrive/My Drive/All_Deep_Learning_Models/BigGANModelEvolution"
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, upsample=False, downsample=False):
super(ResBlock, self).__init__()
self.upsample = upsample
self.downsample = downsample
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
if upsample or downsample or in_channels != out_channels:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
shortcut_x = self.shortcut(x)
if self.upsample:
out = nn.functional.interpolate(out, scale_factor=2)
shortcut_x = nn.functional.interpolate(shortcut_x, scale_factor=2)
if self.downsample:
out = nn.functional.avg_pool2d(out, 2)
shortcut_x = nn.functional.avg_pool2d(shortcut_x, 2)
out += shortcut_x
return self.relu(out)
class BigGANGenerator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, latent_dim=128):
super(BigGANGenerator, self).__init__()
self.latent_dim = latent_dim
self.proj = nn.Linear(latent_dim, 16 * latent_dim * 4 * 4)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(16 * latent_dim * 4 * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.res_blocks = nn.Sequential(
ResBlock(16 * latent_dim, 8 * latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(8 * latent_dim, 4 * latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(4 * latent_dim, 2 * latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(2 * latent_dim, latent_dim, upsample=True),
ResBlock(latent_dim, latent_dim // 2, upsample=True), # Add this layer
ResBlock(latent_dim // 2, latent_dim // 4, upsample=True), # Add this layer
)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(latent_dim // 4, 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = x.view(-1, 16 * self.latent_dim, 4, 4)
x = self.res_blocks(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.tanh(x)
return x
class BigGANDiscriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BigGANDiscriminator, self).__init__()
self.res_blocks = nn.Sequential(
ResBlock(3, 64, downsample=True),
ResBlock(64, 128, downsample=True),
ResBlock(128, 256, downsample=True),
ResBlock(256, 512, downsample=True),
ResBlock(512, 1024, downsample=True),
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.res_blocks(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# Initialize the generator and discriminator objects
generator = BigGANGenerator(latent_dim=128)
discriminator = BigGANDiscriminator()
# Move the generator and discriminator to GPU if available
generator = generator.to(device)
discriminator = discriminator.to(device)
# Set up the optimizers
optimizer_G = optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE , betas=betas)
optimizer_D = optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE , betas=betas)
image_saved_count = 0
g_scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler()
d_scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler()
train_loader = ggd.getdataloaders(batch_size, num_workers)
iterations_per_epoch = ggd.size_of_trainning_dataset // batch_size
evolution_frequency = iterations_per_epoch // evolution_images_per_epoch
if LOAD_MODEL:
rcpf.load_checkpoint(LOAD_CHECKPOINT_GEN, generator, optimizer_G,LEARNING_RATE,)
rcpf.load_checkpoint(LOAD_CHECKPOINT_DISC, discriminator, optimizer_D,LEARNING_RATE,)
def test_discriminator():
ImageHeight, ImageWidth = 128, 128
x = torch.randn((5, 3, ImageHeight, ImageWidth))
test_model = BigGANDiscriminator()
test_model = test_model.to(device)
x = x.to(device)
preds = test_model(x)
print(preds.shape)
test_discriminator()
def test_generator():
# Create a Generator model
test_generator = BigGANGenerator(latent_dim=128)
test_generator = test_generator.to(device)
# Create a random latent vector
z = torch.randn(2, 128).to(device) # or any batch size greater than 1
# Generate an image using the generator
img_generated = test_generator(z)
# Print the generated image shape
print(img_generated.shape)
test_generator()
def test_model(generator, device=device):
generator.eval() # Set the generator to evaluation mode
with torch.no_grad(): # No need to compute gradients for this operation
random_noise = torch.randn(1, 512).to(device) # Create random noise vector
generated_image = generator(random_noise) # Generate image using the generator
# Convert the resized image to a PIL image and display it
image = ToPILImage()(generated_image)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# Define the loss function
def wasserstein_loss(output, target):
return torch.mean(output * target)
def save_images(y_fake, folder, image_saved_count):
save_image(y_fake, f"{folder}/Generated_Image{image_saved_count}.png")
import torch.nn.functional as F
def resize_images(images, size=128):
# Check if the input images have the expected shape
if len(images.shape) != 4:
raise ValueError("Expected input shape: [batch_size, channels, height, width]")
# Rescale the images to the desired size
resized_images = F.interpolate(images, size=(size, size), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
return resized_images
def Test_resize_function(num_images):
toPIL = transforms.ToPILImage()
train_loader = ggd.getdataloaders(num_images, 2) # Set batch size to num_images
for i, test_data in enumerate(train_loader):
# Display the images in a grid
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, num_images, figsize=(20, 2))
for j in range(num_images):
image = test_data[j]
#image = resize_images(image.unsqueeze(0),128)
image = image.squeeze(0)
axs[j].imshow(toPIL(image.cpu()))
axs[j].axis('off')
plt.show()
print(test_data.shape)
break
Test_resize_function(5)
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
def train_BigGAN2(train_loader, epochs, save_file_index):
# Initialize the networks
training_losses = []
validations_losses = []
training_accuracies = []
validation_accuracies = []
global image_saved_count
# Training loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
loop = tqdm(total=len(train_loader), position=0, leave=False)
for i, real_images in enumerate(train_loader):
real_images = real_images.to(device)
batch_size = real_images.size(0)
# Update the discriminator
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
real_labels = Variable(torch.ones(batch_size, 1).to(device))
fake_labels = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, 1).to(device))
# Calculate the discriminator loss for real images
real_output = discriminator(real_images)
real_loss = wasserstein_loss(real_output, real_labels)
# Generate fake images
z = torch.randn(batch_size, 128).to(device)
fake_images = generator(z)
save_image = fake_images
# Calculate the discriminator loss for fake images
fake_output = discriminator(resize_images(fake_images.detach()))
fake_loss = wasserstein_loss(fake_output, fake_labels)
# Calculate the total discriminator loss and update the discriminator
d_loss = torch.mean(fake_loss) - torch.mean(real_loss)
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
# Update the generator
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# Calculate the generator loss
fake_output = discriminator(resize_images(fake_images))
g_loss = wasserstein_loss(fake_output, real_labels)
# Update the generator
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
loop.set_postfix(d_loss=d_loss.item(), g_loss=g_loss.item())
loop.set_description(f"Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{epochs}]") # Update epoch number
loop.update(True) # Refresh the progress bar
if i % evolution_frequency == 0:
save_images(save_image, evolution_folder, image_saved_count)
image_saved_count += 1
if SAVE_MODEL and epoch % 5 == 0:
rcpf.save_checkpoint(generator, optimizer_G , save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_GEN)
rcpf.save_checkpoint(discriminator, optimizer_D, save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_DISC)
save_file_index = save_file_index + 1
loop.close()
return training_losses, training_accuracies
training_accuracies = []
training_losses = []
save_file_index = 0
try:
training_losses, training_accuracies = train_BigGAN2(train_loader, epochs=10000, save_file_index = 1)
except Exception as e :
print(e)
torch.set_printoptions(profile = "default")
import traceback
print(traceback.format_exc())
rcpf.save_checkpoint(generator, optimizer_G , save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_GEN)
rcpf.save_checkpoint(discriminator, optimizer_D, save_file_index, filename= CHECKPOINT_DISC)
# Plotting training losses
fig = plt.figure()
plt.title("Training Losses")
plt.xlabel("Iterations")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.plot(training_losses, label='Training Loss', alpha=.5)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Plotting training and validation accuracies
fig = plt.figure()
plt.title("Training Accuracies")
plt.xlabel("Iterations")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.plot(training_accuracies, label='Training Accuracy', alpha=.5)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
test_model(generator)[/CODE]What did I do wrong ? did I Messed up the wasserstein_loss ?
[CODE title="wasserstein_loss"]def wasserstein_loss(output, target):
return torch.mean(output * target)[/CODE]
why I am getting :
d_loss=-9.95e+3, g_loss=7.18e+3
I started training last night.