Andrea Vironda
- 69
- 3
- TL;DR
- Constraint reactions on a 6 pads system
I would be interested in calculating the constraint reactions on the 6 pads in yellow in the figure, about 300mm apart among them and loaded with F=12500 kN in blue. Since the system is highly hyperstatic, I don't know how to calculate the constraints. Can you give me a hand?
I've made a FEM calculation using Ansys Workbench v18. Do you think it's possible to read those data from there?
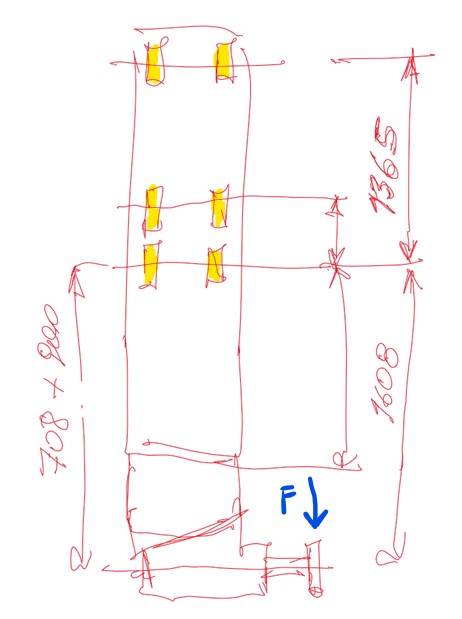
I've made a FEM calculation using Ansys Workbench v18. Do you think it's possible to read those data from there?
Last edited by a moderator: