- #1
trial_
- 1
- 0
Hi, Guys, I am building light electric vehicle for fun and hobby.
I am experimenting with stuff, but have some difficulty calculating a reasonable geometry for the suspension.
It is a SINGLE arm suspension and I am planing to use Fox Float Air Shock with length 190mm, it has pressure control and compression and rebound adjustments. Progressive behavior.
I am attaching a picture with explanation what I am trying to achieve, if somebody can point me in direction how to calculate a linear or slightly progressive geometry I will be super grateful! Also, how to control and change, the progression of the geometry, if I decide to use another type of absorber.
It is NOT meant to be multi linkage geometry, only one rocking part, pretty much a triangle - axis of rotation, travel point and the last point where I mount the shock, which I am looking to calculate somehow.
Thanks a lot :)
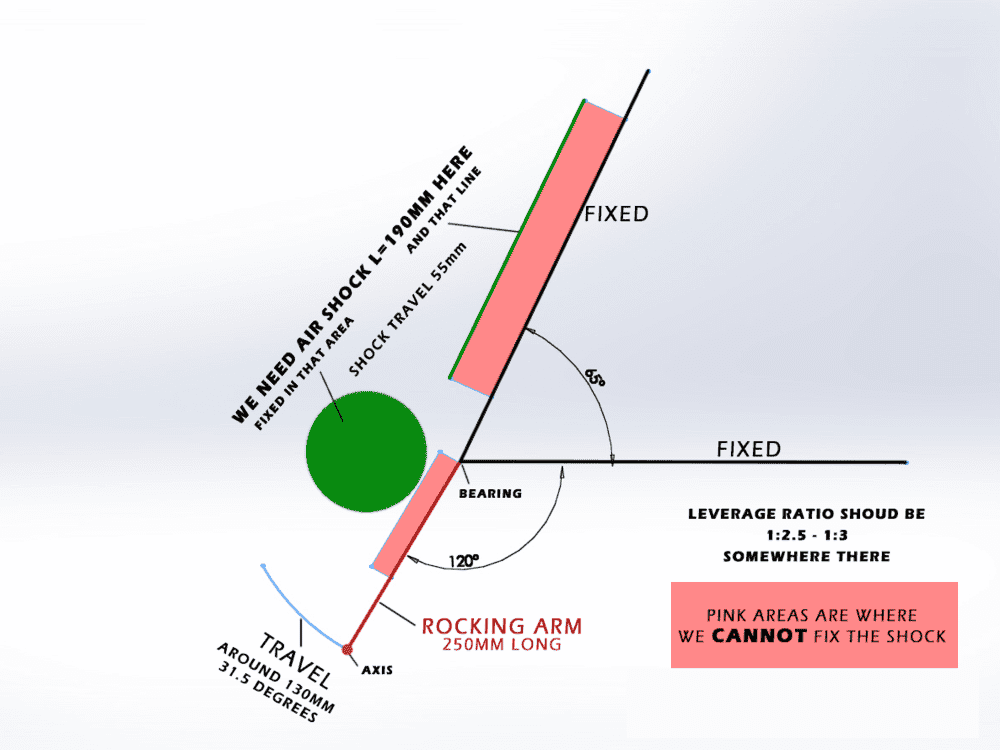
I am experimenting with stuff, but have some difficulty calculating a reasonable geometry for the suspension.
It is a SINGLE arm suspension and I am planing to use Fox Float Air Shock with length 190mm, it has pressure control and compression and rebound adjustments. Progressive behavior.
I am attaching a picture with explanation what I am trying to achieve, if somebody can point me in direction how to calculate a linear or slightly progressive geometry I will be super grateful! Also, how to control and change, the progression of the geometry, if I decide to use another type of absorber.
It is NOT meant to be multi linkage geometry, only one rocking part, pretty much a triangle - axis of rotation, travel point and the last point where I mount the shock, which I am looking to calculate somehow.
Thanks a lot :)