noname1
- 131
- 0
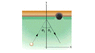
The figure below gives an overhead view of the path taken by a 0.165 kg cue ball as it bounces from the rail of a pool table. The ball's initial speed is 2.00 m/s, and the angle θ1 = 30.0°. The bounce reverses the y component of the ball's velocity but does not alter the x component.
(b) What is the change in the ball's linear momentum in unit-vector notation? (The fact that the ball rolls is irrelevant to the question.)
I tried solving the one that wrong by 2*0.165*2*cos(30) = -5.72j but when i submit the answer is saying its wrong
what am i doing wrong
(b) What is the change in the ball's linear momentum in unit-vector notation? (The fact that the ball rolls is irrelevant to the question.)
I tried solving the one that wrong by 2*0.165*2*cos(30) = -5.72j but when i submit the answer is saying its wrong
what am i doing wrong