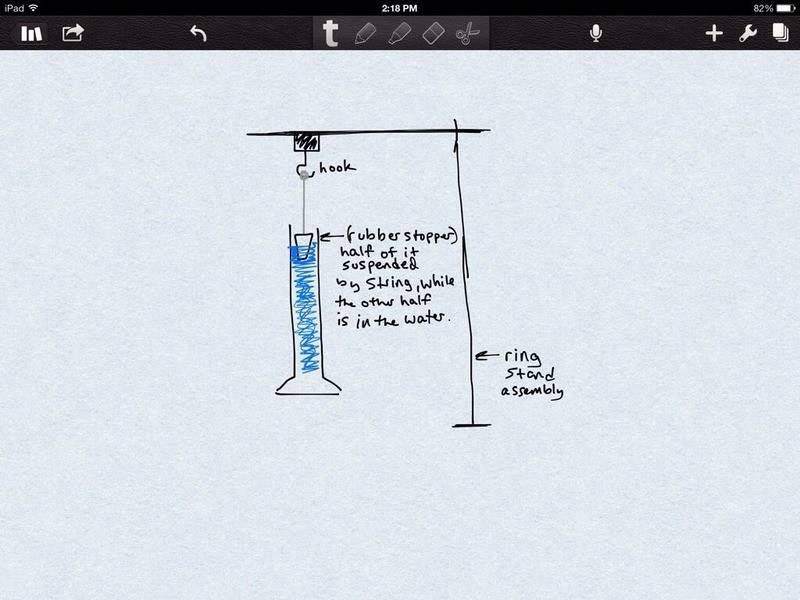
SUMMARY
This discussion focuses on calculating the tension in a string suspending a rubber stopper that is half-submerged in water. The key concepts include buoyant force, which is calculated using the formula ρ x V x g, where ρ is the density of water (1000 kg/m³), V is the displaced volume, and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The tension in the string (T) can be determined using the equation T = W - F_b, where W is the weight of the stopper and F_b is the buoyant force. The discussion emphasizes the importance of understanding Archimedes' Principle in determining the buoyant force when only part of the object is submerged.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Archimedes' Principle
- Knowledge of buoyant force calculations
- Familiarity with free body diagrams (FBDs)
- Basic physics concepts related to weight and density
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Archimedes' Principle in various scenarios
- Learn how to calculate buoyant force for partially submerged objects
- Explore advanced free body diagram techniques for complex systems
- Investigate the effects of different densities on buoyancy calculations
USEFUL FOR
Students in AP Physics, educators teaching buoyancy concepts, and anyone interested in understanding the principles of tension and buoyancy in fluid mechanics.