SUMMARY
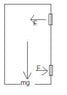
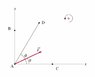
The discussion focuses on calculating the torque exerted by hinges on a door measuring 2.30m in height and 1.30m in width, with a mass of 13.0kg. The hinges are positioned 0.40m from the top and bottom, each supporting half the door's weight. Participants emphasize the importance of equilibrium in torque calculations, noting that only the horizontal component of the hinge force contributes to torque about the other hinge. A detailed analysis of force components and the use of Free Body Diagrams (FBD) are recommended for solving the problem.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of torque and equilibrium in static systems
- Familiarity with Free Body Diagrams (FBD)
- Knowledge of vector cross products in physics
- Basic principles of statics and force components
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of torque calculation using the equation τ = r × F
- Learn how to construct and analyze Free Body Diagrams (FBD) for static systems
- Explore the concept of equilibrium in mechanical systems and its applications
- Investigate the effects of different force components on torque and equilibrium
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, mechanical engineers, and anyone interested in understanding the mechanics of static systems and torque calculations.