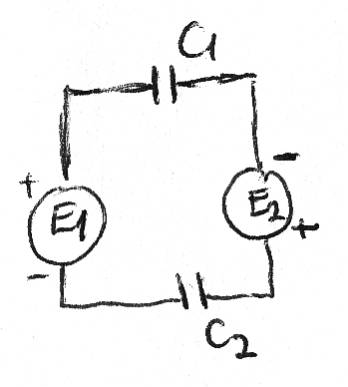
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the behavior of capacitors in a circuit with multiple voltage suppliers, specifically focusing on how the capacitors charge when connected in series. Participants explore different cases based on the relationship between the voltage sources and the implications for the charging process.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants assert that capacitors in series will charge when connected to multiple voltage sources, with the total voltage being the sum of the sources.
- Others clarify that capacitors do not "charge" in the traditional sense, but rather become energized due to the imbalance of electrons between their plates.
- A participant questions whether the presence of two voltage sources affects the charging process compared to a single source, particularly in terms of current flow and voltage measurement across the capacitors.
- Some participants discuss the implications of having one capacitor removed from the circuit, questioning whether the remaining capacitor can still energize if the circuit is interrupted.
- There is mention of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and its application to the circuit, with some participants expressing difficulty in applying it to capacitors as opposed to resistors.
- One participant notes that without resistance, the capacitors would charge instantly, leading to a brief pulse of current before stabilizing.
- Another participant emphasizes that the circuit must be complete for a capacitor to energize, indicating the importance of a closed loop for current flow.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the nature of charging in capacitors and the effects of multiple voltage sources. There is no consensus on whether the charging process behaves the same way with one or two voltage suppliers, and the discussion remains unresolved regarding the implications of removing a capacitor from the circuit.
Contextual Notes
Some participants highlight the need for practical considerations such as series resistance, while others focus on idealized scenarios. The discussion includes assumptions about the initial conditions of the capacitors and the nature of the voltage sources.