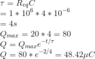SUMMARY
The discussion centers on analyzing the charging of a capacitor after changing the switch position in a circuit. When the switch is in position A, the voltage across the capacitor (Vc) is 0V due to prolonged connection, and the current (I) is calculated as 2 x 10^-5 A. Upon switching to position B, applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) yields a charge (Q) of 80μC on the capacitor, calculated using the formula Q = CV with C being 4 x 10^-6 F. The initial confusion regarding the time variable (t=2s) is clarified, confirming the calculations are correct without needing to reference time.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)
- Familiarity with capacitor charging equations (Q = CV)
- Basic knowledge of electric current and voltage relationships (V = IR)
- Concept of steady-state conditions in electrical circuits
NEXT STEPS
- Study the implications of time constants in RC circuits
- Learn about transient analysis in capacitor circuits
- Explore advanced applications of Kirchhoff's laws in complex circuits
- Investigate the effects of varying capacitance on charge and voltage
USEFUL FOR
Students in electrical engineering, circuit designers, and anyone studying capacitor behavior in DC circuits will benefit from this discussion.