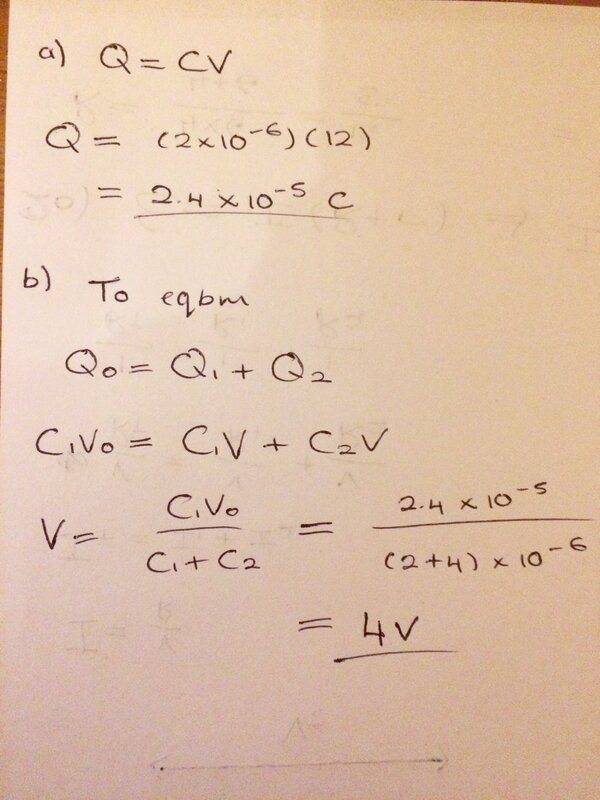SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the behavior of capacitors when a charged capacitor is connected to an uncharged capacitor. Specifically, a 4 μF capacitor is connected to a 2 μF capacitor, leading to a redistribution of charge. The conclusion drawn is that the total charge is shared among the capacitors, resulting in each capacitor being charged to one-third of the voltage required for the 2 μF capacitor alone. This intuitive approach simplifies the understanding of charge distribution in capacitors in parallel.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of capacitor charge distribution
- Knowledge of capacitance values (e.g., microfarads)
- Familiarity with parallel capacitor configurations
- Basic electrical circuit theory
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of capacitor charge sharing in parallel circuits
- Explore the mathematical calculations for voltage and charge in capacitors
- Learn about the effects of different capacitance values on charge distribution
- Investigate real-world applications of capacitors in electronic circuits
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electrical engineering, electronics enthusiasts, and anyone interested in understanding capacitor behavior in circuits.