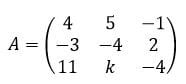Yankel
- 390
- 0
Hi all,
I have the matrix A shown in the attached photo.
View attachment 3667
I need to check for which values of k, the matrix A^3 is invertible.
I tried calculating A^3, by multiplying A by itself twice. I got a nasty matrix. It makes no sense to me that now I am suppose to find it's rank, by using operations on rows. Am I missing something ? How would you solve this in the easiest way ?
Thanks !
I have the matrix A shown in the attached photo.
View attachment 3667
I need to check for which values of k, the matrix A^3 is invertible.
I tried calculating A^3, by multiplying A by itself twice. I got a nasty matrix. It makes no sense to me that now I am suppose to find it's rank, by using operations on rows. Am I missing something ? How would you solve this in the easiest way ?
Thanks !