Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the conservation of momentum in systems of particles, particularly focusing on how momentum is conserved in collisions involving multiple particles. Participants explore the implications of Newton's laws and the mathematical proofs related to momentum conservation in both two-body and n-body systems.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants assert that momentum is conserved in collisions when no external forces are applied, referencing Newton's third law.
- Others question the clarity of the initial inquiry regarding how momentum conservation applies to a system of n particles.
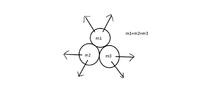
- A participant argues that while momentum is conserved for the entire system, it is not necessarily conserved pairwise for three or more bodies.
- Another participant provides a mathematical proof showing that the total momentum remains constant when external forces are absent, using Newton's second and third laws.
- Some participants discuss the implications of external forces on momentum conservation, suggesting that the presence of external forces complicates the conservation laws.
- Analogies involving bank accounts are introduced to illustrate the concept of conservation in a system, although some participants express confusion about the implications of these analogies.
- There is a discussion about the validity of pairwise conservation in the context of multiple transactions, with differing opinions on whether this analogy accurately represents momentum conservation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree that momentum is conserved in a closed system without external forces, but there is disagreement regarding the interpretation of pairwise conservation in systems with multiple particles. The discussion remains unresolved on the implications of the analogies used.
Contextual Notes
Some participants note that the mathematical proof for n-body systems is more complex than for two-body systems, and there are discussions about the assumptions made regarding external forces and their effects on momentum conservation.