SUMMARY
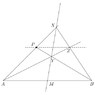
This discussion focuses on constructing a line through an arbitrary point P that is parallel to a given line segment AB using only an unmarked straight edge. The midpoint M of AB is utilized in the construction process. Participants detail the steps to find intersection points X and Y, leading to the identification of point Z, which confirms that line PZ is parallel to AB. The construction ultimately connects point P to the harmonic conjugate of M on line AB, demonstrating a practical application of Ceva's theorem.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of geometric constructions using straight edges
- Familiarity with the concepts of midpoints and parallel lines
- Knowledge of harmonic conjugates in projective geometry
- Basic principles of Ceva's theorem
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of harmonic conjugates in projective geometry
- Explore advanced geometric constructions using unmarked straight edges
- Learn about the applications of Ceva's theorem in various geometric contexts
- Investigate the implications of parallel lines in Euclidean geometry
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, geometry enthusiasts, and educators interested in advanced geometric constructions and theorems related to parallel lines and harmonic conjugates.