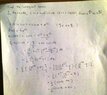Contour integral (please check my solution)
- Context: MHB
- Thread starter aruwin
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Contour integral Integral
Click For Summary
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around a contour integral solution, specifically addressing the interpretation of the contour limits "from e^-pi*1/2 to e^pi*i/2" and its implications for the calculation involved.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant requests verification of their solution and expresses uncertainty about the contour limits.
- Some participants affirm the correctness of the solution while suggesting simplifications based on the property that $\sin\pi = 0$.
- Another participant seeks clarification on the meaning of the contour limits and their impact on the calculation.
- It is explained that the contour starts at $e^{-i\pi/2} = -i$ and ends at $e^{i\pi/2} = i$ on the unit circle.
- A participant questions whether the contour limits affect the calculation and why integration occurs from -pi/2 to pi/2.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the correctness of the solution but have differing views on the implications of the contour limits and their effect on the integration process. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the impact of these limits on the calculation.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved questions about the significance of the contour limits and their relationship to the integration bounds, which may depend on specific definitions or interpretations of the contour integral.
Similar threads
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 14 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
Undergrad
Fourier coefficients of convolution
- · Replies 1 ·
Graduate
Complex Analysis: Contour Integral
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 27 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 6 ·
- · Replies 2 ·