MechatronO
- 30
- 1
I've been looking around for formulas on how to calculate different aspects of DC motors and buck converters such as average current.
The reason is that I'm about to pick switch frequency for a motor, and don't know what characterics I can expect if I alter the switch frequency. Papers and publications regarding this are very much appreciated, as I haven't yet found any that answer my questions.
I succeded in coming up with a formula for the max current through a switched RL circuit with a freewheeling diode(essentially a DC motor with the emf substracted from the input voltage), related to PWM period and duty as
Imax = \frac{E}{R} (1-e-RDT/L/(1-e-RT/L)
Where R is the circuits resistance, L is the inductance, D is the duty ranging from 0-1 and T is period time.
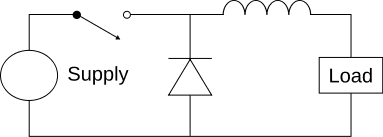
The circuit would look like this, with the load replaced by a resistor:
The output current would look like the non-square wave in this diagram:
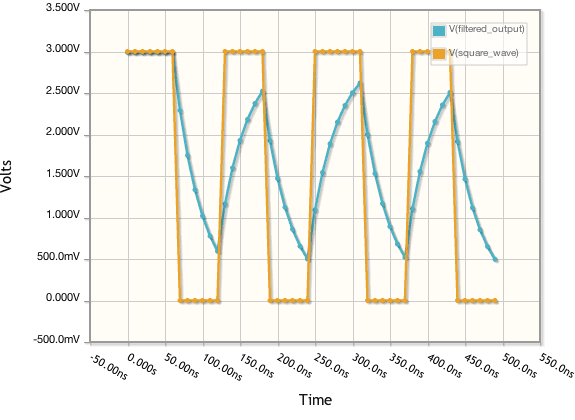
I think its correct, at least the endpoints are as they should. If somebody is interested I'll can post the derivation for this one and a similar formula for Imin.
I was about to determine a formula for Iavg as well, however I decided to instead look for established info.
So, publications, formulas and personal experience regarding DC motor characteristics related to switch frequency are very much wanted. I'm especially interested in a formula that relates Iavg to switch frequency and duty cycle.
The reason is that I'm about to pick switch frequency for a motor, and don't know what characterics I can expect if I alter the switch frequency. Papers and publications regarding this are very much appreciated, as I haven't yet found any that answer my questions.
I succeded in coming up with a formula for the max current through a switched RL circuit with a freewheeling diode(essentially a DC motor with the emf substracted from the input voltage), related to PWM period and duty as
Imax = \frac{E}{R} (1-e-RDT/L/(1-e-RT/L)
Where R is the circuits resistance, L is the inductance, D is the duty ranging from 0-1 and T is period time.
The circuit would look like this, with the load replaced by a resistor:
The output current would look like the non-square wave in this diagram:
I think its correct, at least the endpoints are as they should. If somebody is interested I'll can post the derivation for this one and a similar formula for Imin.
I was about to determine a formula for Iavg as well, however I decided to instead look for established info.
So, publications, formulas and personal experience regarding DC motor characteristics related to switch frequency are very much wanted. I'm especially interested in a formula that relates Iavg to switch frequency and duty cycle.