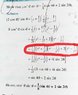De moivre's theorem complex number
- Thread starter kelvin macks
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Complex Complex number Theorem
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the application of the distributive law in the context of complex numbers, specifically relating to De Moivre's Theorem. The equation presented, (a+b)c = ac+bc, where a=z²+1/z², b=2, and c=z²-1/z², illustrates a higher-order form of Morrie's Law, as referenced by Richard Feynman. The author emphasizes that the manipulation of these terms is not directly tied to complex numbers but rather to algebraic principles. The conversation highlights the importance of understanding foundational algebraic laws in mathematical proofs.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of algebraic identities, specifically the distributive law.
- Familiarity with complex numbers and their properties.
- Knowledge of De Moivre's Theorem and its applications.
- Basic concepts of mathematical proofs and theorems.
- Study the applications of De Moivre's Theorem in complex number calculations.
- Explore Morrie's Law and its implications in higher-order algebra.
- Learn about the proof of Urquhart's Theorem and its geometric significance.
- Investigate Richard Feynman's contributions to mathematics and physics, focusing on his early insights.
Mathematicians, educators, students of algebra, and anyone interested in the foundational principles of complex numbers and their applications in proofs.
Similar threads
Insights
Views On Complex Numbers
- · Replies 108 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
Undergrad
Euler, De Moivre and a printing error
- · Replies 2 ·
High School
Getting from complex domain to real domain
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 10 ·
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 6 ·
High School
Inequalities of complex number
- · Replies 6 ·