jsg94
- 8
- 0
Good evening everyone,
I have a pressure meter from where we determined a pressure drop of 5.5 psi (Initial pressure 45.5 psi, final pressure 40 psi). The working fluid is air. The diameter of one of the hoses that is connected to the pressure meter is 1/4". I wasn't able to take a picture of the setup but I attached a quick drawing I made. The other diameter (i.e. D2) is still unknown but can be easily measured if necessary. We need to calculate the flow rate based on this information.
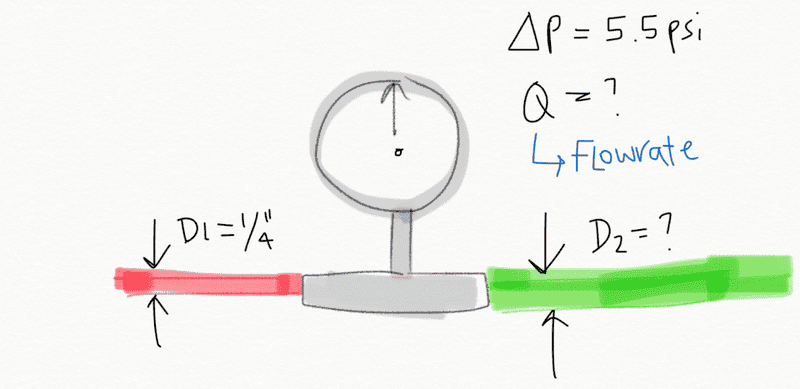
I know that with incompressible fluids it's easier to determine the Flow rate, since it can be approximated as the square root of the pressure difference across the pressure meter. But I suppose this wouldn't be a good assumption for compressible fluids. I was trying to use the Bernoulli equation but then again, in my Fluids book it is specified that "We assume the flow is horizontal (z1 = z2), steady, inviscid, and incompressible between points (1) and (2)". The following equations are shown:
EQUATION 1.
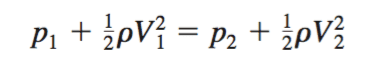
EQUATION 2.
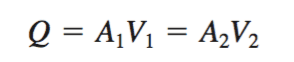
EQUATION 3.
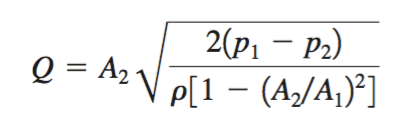 Would it be possible to use these equations and use air as an incompressible fluid? I tried going over the chapter on my book that covered compressible fluids but it was no help. I couldn't find what I was looking for. Any ideas? I would really appreciate your help!
Would it be possible to use these equations and use air as an incompressible fluid? I tried going over the chapter on my book that covered compressible fluids but it was no help. I couldn't find what I was looking for. Any ideas? I would really appreciate your help!
I have a pressure meter from where we determined a pressure drop of 5.5 psi (Initial pressure 45.5 psi, final pressure 40 psi). The working fluid is air. The diameter of one of the hoses that is connected to the pressure meter is 1/4". I wasn't able to take a picture of the setup but I attached a quick drawing I made. The other diameter (i.e. D2) is still unknown but can be easily measured if necessary. We need to calculate the flow rate based on this information.
I know that with incompressible fluids it's easier to determine the Flow rate, since it can be approximated as the square root of the pressure difference across the pressure meter. But I suppose this wouldn't be a good assumption for compressible fluids. I was trying to use the Bernoulli equation but then again, in my Fluids book it is specified that "We assume the flow is horizontal (z1 = z2), steady, inviscid, and incompressible between points (1) and (2)". The following equations are shown:
EQUATION 1.
EQUATION 2.
EQUATION 3.