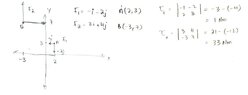Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around determining the point of application of a resultant force, specifically in the context of calculating moments and understanding the relationship between forces and torques. The original poster expresses difficulty with part b of the question, having previously calculated the components of the given forces in part a.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking, Conceptual clarification
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the calculation of moments using vector cross multiplication and question the relevance of this step. There are inquiries about the necessity of equilibrium in the problem setup and the interpretation of negative torque values. The original poster seeks clarification on how to find the coordinates for the point where the resultant force acts.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants providing insights into the calculations of forces and torques. Some guidance has been offered regarding the relationship between resultant forces and torques, and the need for further exploration of the conditions under which these calculations hold true. Multiple interpretations of the problem are being examined.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that the question does not specify whether the system is in equilibrium, which has implications for their calculations. There is also mention of practice questions and solutions being available, which may influence the discussion dynamics.