crushedcorn
- 7
- 0
This question was posted on Khan Academy. I attempted it after watching all of their great Work and Energy videos, but the way they arrived at the answer was way above my skill level even after reviewing the videos a number of times. Here is the question:
What is the minimum height h of a slope that must be constructed in order for a rider in the cart with a combined mass m = 80.0 kg to complete the loop with a radius r = 10.0 meters safely, assuming a frictionless trip?
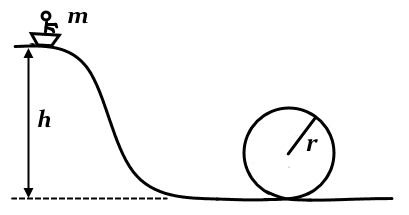
How would you answer this question? The way that they arrived at their answer is below. Is there any alternative/more concise way to arrive at the same answer? I would have never guessed to proceed in the way noted in Hint #3.
We can use the Conservation of Energy formula to evaluate these two points: at the top of the hill and at the top of the loop.
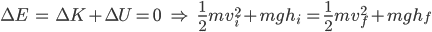
Hint #2
At the top of the hill, the kinetic energy is zero, and the potential energy is mgh.
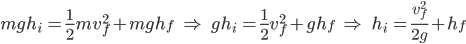
Hint #3
At the top of the loop, we must derive another formula to connect ideas together by using Newton’s Second Law to describe the forces acting on the cart and then to solve for v:
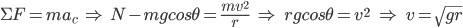
Hint #4
This expression is for the velocity at the top of the loop since there is no normal force only at that point. Additionally, h = 2r such that the potential energy is mg(2r).

Hint #5
The correct answer is 2.5. Since the radius of the loop is 10 meters, then 2.5r is 25 meters.
What is the minimum height h of a slope that must be constructed in order for a rider in the cart with a combined mass m = 80.0 kg to complete the loop with a radius r = 10.0 meters safely, assuming a frictionless trip?
How would you answer this question? The way that they arrived at their answer is below. Is there any alternative/more concise way to arrive at the same answer? I would have never guessed to proceed in the way noted in Hint #3.
We can use the Conservation of Energy formula to evaluate these two points: at the top of the hill and at the top of the loop.
Hint #2
At the top of the hill, the kinetic energy is zero, and the potential energy is mgh.
Hint #3
At the top of the loop, we must derive another formula to connect ideas together by using Newton’s Second Law to describe the forces acting on the cart and then to solve for v:
Hint #4
This expression is for the velocity at the top of the loop since there is no normal force only at that point. Additionally, h = 2r such that the potential energy is mg(2r).
Hint #5
The correct answer is 2.5. Since the radius of the loop is 10 meters, then 2.5r is 25 meters.