PainterGuy
- 938
- 73
Hi,
I cannot figure out how they got Table 2.1. For example, how come when x=1, F_X(x)=1/2? Could you please help me with it?
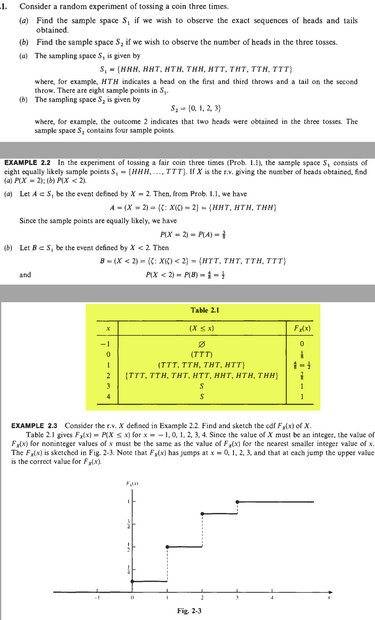
Hi-resolution copy of the image: https://imagizer.imageshack.com/img923/2951/w9yTCQ.jpg
I cannot figure out how they got Table 2.1. For example, how come when x=1, F_X(x)=1/2? Could you please help me with it?
Hi-resolution copy of the image: https://imagizer.imageshack.com/img923/2951/w9yTCQ.jpg