SUMMARY
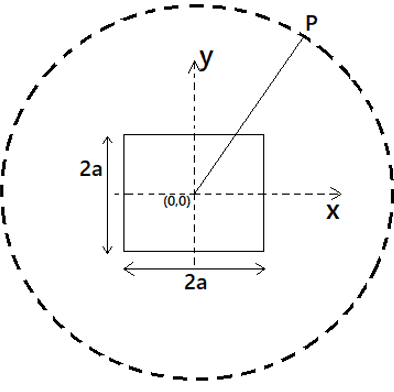
This discussion centers on the application of Gauss's law to determine the electric field at a point P using a Gaussian surface. It is established that while any closed surface can be selected, the electric field must be constant across that surface for the law to be applied effectively. The conversation highlights a misunderstanding regarding the symmetry of the electric field generated by a square line charge, which is not spherically symmetric, leading to incorrect assumptions about the electric field's constancy during integration.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Gauss's law in electrostatics
- Familiarity with electric field concepts and charge distributions
- Knowledge of symmetry in electric fields
- Basic calculus for integration in physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Gauss's law with various charge distributions
- Learn about highly-symmetrical charge configurations and their electric fields
- Review integration techniques for electric fields over closed surfaces
- Explore the concept of electric field symmetry and its implications in electrostatics
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, particularly those studying electromagnetism, educators explaining Gauss's law, and anyone interested in understanding electric fields and charge distributions.