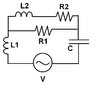
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the relationship between mechanical systems and electrical circuits, specifically through the lens of impedance and differential equations. Participants analyze the damping forces on two masses, m1 and m2, and relate them to electrical components using an electromechanical analogy. Key formulas discussed include the conversion of mechanical quantities to electrical equivalents, such as q ~ x, i ~ v, k ~ 1/C, L ~ m, and b ~ R. The impedance is calculated from the equivalent circuit formed by these relationships, emphasizing the importance of understanding both the physical and mathematical aspects of the problem.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of differential equations in mechanical systems
- Familiarity with electromechanical analogies
- Knowledge of electrical circuit components (resistors, inductors, capacitors)
- Basic principles of impedance in AC circuits
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of impedance in complex form: Z_R = R, Z_L = jLω, Z_C = -j/(Cω)
- Learn about the electromechanical analogy in detail, focusing on mass-spring-damper systems
- Explore circuit analysis techniques for combined series and parallel RLC circuits
- Review differential equations related to mechanical systems and their electrical counterparts
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics and engineering, particularly those specializing in electrical engineering, mechanical systems, and circuit analysis.