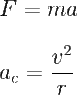SUMMARY
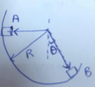
The discussion focuses on calculating the normal force acting on a 1 kg object moving along a circular frictionless path with a radius of 0.5 m at an angle of 30° from the vertical. The correct calculation reveals that the normal force at point B is 25.98 N. Participants corrected initial mistakes in the energy conservation equation, specifically the misapplication of variables and the height calculation at point B. The final consensus confirms the answer as 25.98 N.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of circular motion dynamics
- Knowledge of energy conservation principles
- Familiarity with gravitational potential energy calculations
- Basic algebra for solving equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of circular motion in physics
- Learn about gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy relationships
- Explore the concept of normal force in different scenarios
- Practice solving problems involving energy conservation in circular paths
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and energy conservation, as well as educators looking for problem-solving examples in circular motion.