SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the implications of the Friedmann equations in cosmology, particularly regarding the spatial curvature parameter, k. It is established that a flat universe (k=0) is a theoretical null set, as measurements cannot confirm k to be exactly zero. The conversation highlights that if the critical density (ρ=ρc) is satisfied, then k cannot be ±1, reinforcing that k must equal 0. The participants emphasize the mathematical relationships governing the universe's expansion and the conditions under which these relationships hold true.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Friedmann equations in cosmology
- Knowledge of critical density (ρc) and its implications
- Familiarity with spatial curvature parameters (k=0, k>0, k<0)
- Basic grasp of Einstein's field equations and their application to the FRW metric
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Friedmann equations in detail, focusing on their derivations and implications
- Explore the concept of critical density and its role in cosmological models
- Investigate the relationship between curvature parameters and the universe's expansion dynamics
- Review peer-reviewed papers on cosmological models to understand the mathematical foundations
USEFUL FOR
Astronomers, cosmologists, and physics students interested in the mathematical foundations of the universe's expansion and the implications of curvature in cosmological models.
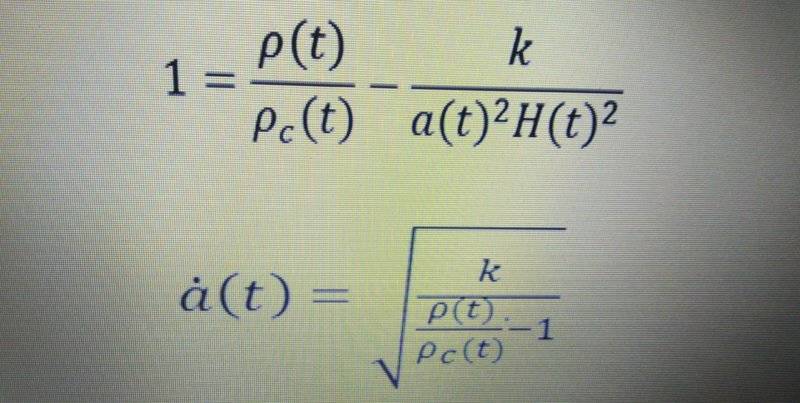
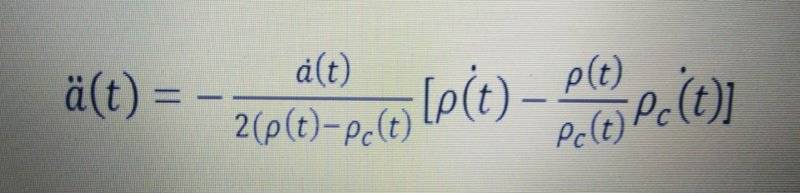 For a flat universe with k=0 and ρ=ρc ,da/dt becomes undefined and d2a/dt2 becomes 0
For a flat universe with k=0 and ρ=ρc ,da/dt becomes undefined and d2a/dt2 becomes 0