SUMMARY
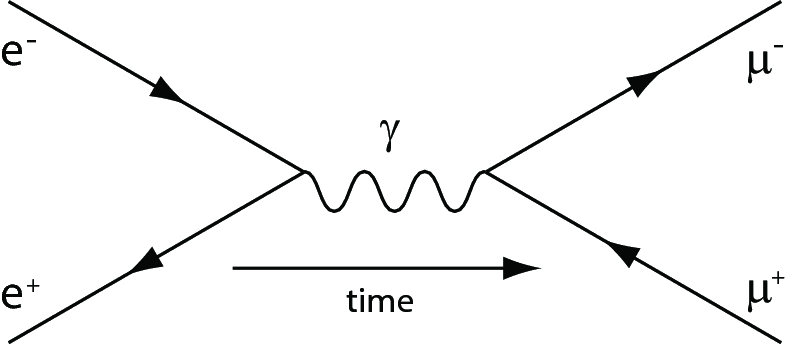
The discussion centers on the electron-positron annihilation process into muons, represented by the Feynman diagram for the reaction $$e^{+}e^{-}\rightarrow \mu^{+}\mu^{-}$$. It is established that only s-channel diagrams are valid for this process due to lepton flavor conservation, which prohibits t-channel and u-channel diagrams in Quantum Electrodynamics (QED). The interaction term in the Lagrangian, $$\mathcal{L}_{\text{int}}=e (\overline{\psi}_e \gamma^{\mu} \psi_e + \overline{\psi}_{\mu} \gamma^{\mu} \psi_{\mu}) A_{\mu}$$, is crucial for understanding the Feynman rules governing these interactions. Additionally, the discussion touches on the impossibility of direct coupling between Dirac fermion fields due to lepton conservation, a fundamental principle in the Standard Model.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Feynman diagrams and their significance in particle physics.
- Familiarity with Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) principles.
- Knowledge of the Standard Model, particularly lepton conservation laws.
- Basic grasp of Lagrangian mechanics and interaction terms in quantum field theory.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation and implications of the interaction term $$\mathcal{L}_{\text{int}}$$ in QED.
- Explore the concept of lepton flavor conservation and its role in particle interactions.
- Investigate effective field theories and their applications, particularly in four-fermion interactions.
- Learn about the implications of Fermi's theory of beta decay in the context of particle physics.
USEFUL FOR
Particle physicists, theoretical physicists, and students studying quantum field theory who seek to deepen their understanding of particle interactions and conservation laws in the Standard Model.