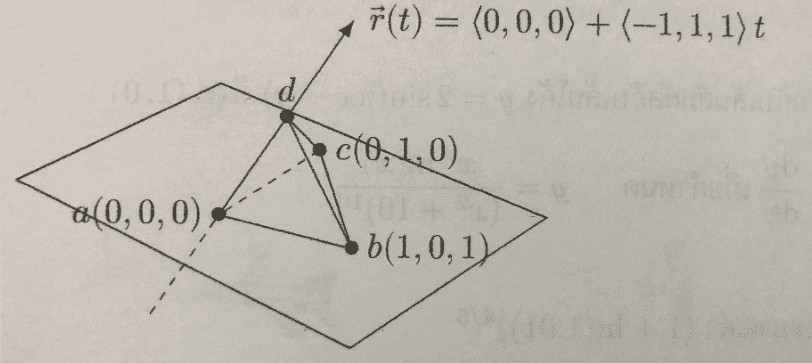Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around finding the coordinates of point D on a line defined by the equation r(t) = (0,0,0) + (-1,1,1)t, such that the volume of the triangular pyramid formed by points A(0,0,0), B(1,0,1), C(0,1,0), and D is equal to 4 cubic units. The context includes geometric calculations related to the volume of pyramids and the properties of planes in three-dimensional space.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
Main Points Raised
- Post 1 introduces the problem of determining point D on the specified line to achieve a pyramid volume of 4 cubic units.
- Post 2 provides a detailed calculation of the base area B of triangle ABC and the volume V of the pyramid, using the formula V = (1/3)Bh, and derives the height h as a projection onto the normal vector of the plane.
- Post 2 concludes that the value of t is 12, leading to the coordinates of point D being (-12,12,12).
- Post 4 presents an alternative approach using the distance formula from a point to a plane, arriving at the same conclusion for t as 12, thus confirming the coordinates of point D.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants appear to agree on the calculations leading to the conclusion that point D is at (-12,12,12) based on different methods, though the discussion does not explore any competing views or alternative solutions.
Contextual Notes
The discussion relies on specific assumptions about the geometric properties of the pyramid and the plane, as well as the correctness of the mathematical derivations presented. No alternative methods or potential errors in the calculations are discussed.