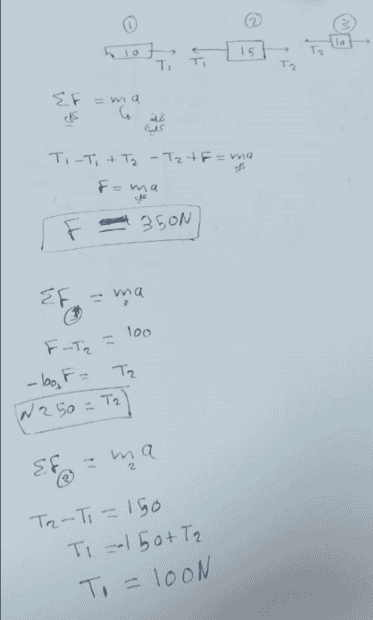Homework Help Overview
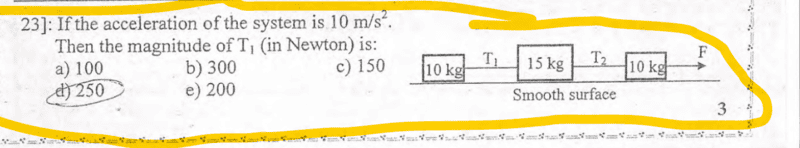
The problem involves determining the tension in ropes connecting three masses being pulled on a surface, with participants discussing their differing answers and approaches to the problem.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants share their calculated tensions, with one suggesting a value of 100 N and others proposing 250 N. Questions arise regarding the relationship between forces and tensions, as well as the analysis of the forces acting on the masses.
Discussion Status
Some participants have offered insights into the relationships between forces and tensions, while others are exploring the implications of connected masses and their accelerations. There is a recognition of differing interpretations and calculations without a clear consensus on the correct tension values.
Contextual Notes
Participants are considering the effects of inextensible strings and the absence of friction in their analyses. There is also mention of the need for a free body diagram to clarify forces acting on the masses.