SUMMARY
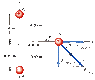
The discussion focuses on calculating the net force on a point charge Q=7μC due to two point charges, q1=3μC and q2=-3μC, in a dipole configuration. The initial approach using the dipole electric field formula, Edipole = kqs/r^3, is incorrect for this scenario as it applies only at large distances. Instead, the correct method involves calculating the individual forces exerted by each charge on Q and then using vector addition to determine the net force.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Coulomb's Law and electric forces
- Familiarity with vector addition in physics
- Knowledge of dipole electric fields and their limitations
- Basic principles of electrostatics
NEXT STEPS
- Study Coulomb's Law for point charges
- Learn about vector addition in physics
- Explore the limitations of dipole electric field equations
- Investigate the concept of electric field lines and their implications
USEFUL FOR
Students in physics courses, particularly those studying electrostatics, as well as educators looking for practical examples of force calculations in dipole systems.