- #1
tomrja
- 18
- 0
Homework Statement
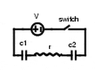
Two capacitors (c1 = 11 and c2 = 15 μF) are charged in series by a 11 V battery. Find the time constant of the charging circuit. (r = 4 Ω).
Homework Equations
V=E(1-e^(-t/T)) Where T=Tau=RC, E is the Voltage of the power source, and V is the voltage of the capacitor.
The Attempt at a Solution
I am fairly certain that Tau is the time constant in this case, so I solved for Tau, but I don't know what to plug in for the voltage of the capacitor (V). Am I even headed in the right direction with this?