hb2325
- 19
- 0
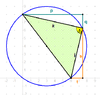
Points (6,0) and (O,8) are the endpoints of the hypotenuse of a
right-angled triangle, whose other vertex is at (x,y). What equation relates x
and y?Attempt at solution:
So What I am thinking is that the line will be perpendicular to the line with end points 6,0 and 0,8.
So The gradient of this line is 4/3, hence the gradient of the other line perpendicular to this one will be -3/4
So the equation relating X and y is y = -3/4 x + c ?
Now can I assume that given line is a perpendicular bisector to the hypotenuse and so interesects it at 3,4 (mid point) and hence substitue for c - which i get to 25/4
So y = -3/4 x + 25/4 , This kinda feels wrong and I would appreciate input.
Thanks.
right-angled triangle, whose other vertex is at (x,y). What equation relates x
and y?Attempt at solution:
So What I am thinking is that the line will be perpendicular to the line with end points 6,0 and 0,8.
So The gradient of this line is 4/3, hence the gradient of the other line perpendicular to this one will be -3/4
So the equation relating X and y is y = -3/4 x + c ?
Now can I assume that given line is a perpendicular bisector to the hypotenuse and so interesects it at 3,4 (mid point) and hence substitue for c - which i get to 25/4
So y = -3/4 x + 25/4 , This kinda feels wrong and I would appreciate input.
Thanks.