cherry
- 25
- 6
- Homework Statement
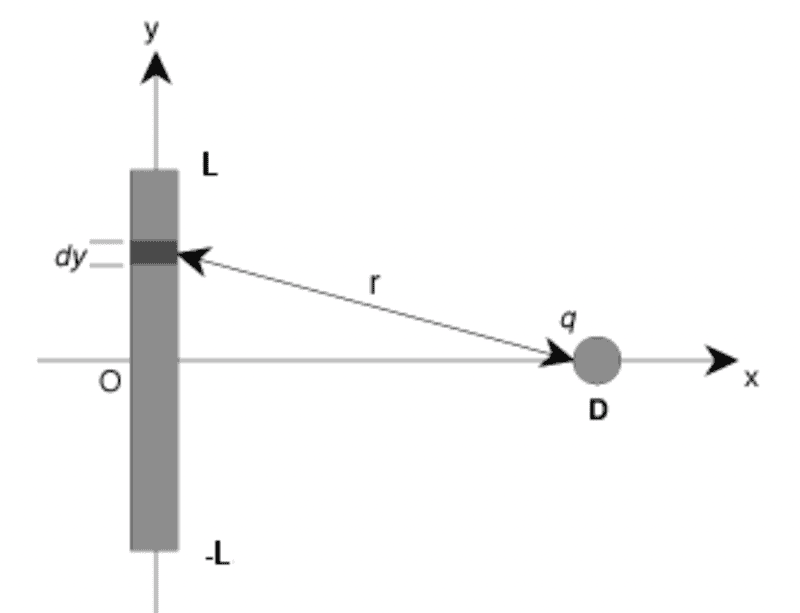
- An electric charge of Q = 6.4 C is distributed uniformly along a rod of length 2L, extending from y = -15.6 cm to y = +15.6 cm, as shown in the diagram. A charge q = 3.05 C, and the same sign as Q, is placed at (D,0), where D = 44 cm. Integrate to compute the total force on q in the x-direction.
- Relevant Equations
- dF=(kqQ/2Lr^2)dy
Hi! My attempt at this solution was:
∫dF = k*q*Q / 2L ∫ (1/r^2) dy
and we know that r^2 = D^2 + y^2 based on the diagram.
Here is where I start getting confused.
I looked at a different physics forum post and the mentor gave this equation:
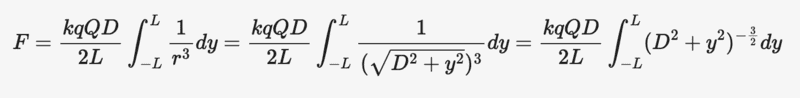
I am mainly confused with the math.
How did he end up with R^(-3) inside the integral?
Otherwise, I ended up solving the integral and getting the right answer.
Thanks!
∫dF = k*q*Q / 2L ∫ (1/r^2) dy
and we know that r^2 = D^2 + y^2 based on the diagram.
Here is where I start getting confused.
I looked at a different physics forum post and the mentor gave this equation:
I am mainly confused with the math.
How did he end up with R^(-3) inside the integral?
Otherwise, I ended up solving the integral and getting the right answer.
Thanks!