robertjford80
- 388
- 0
Homework Statement
The Attempt at a Solution
Obviously brackets mean something other than parentheses because .5[0 + 0] ≠ .5
The discussion focuses on the convergence of Fourier series at points of discontinuity, specifically referencing Dirichlet's theorem as it applies to periodic functions. It establishes that if a periodic function f(x) is piecewise continuous and has left and right derivatives within the interval -π to π, then its Fourier series converges to f(x) at all points except for discontinuities. At these points, the series converges to the average of the left and right limits. The conversation also clarifies the notation used in Fourier series, emphasizing the distinction between the function and its series representation.
PREREQUISITESMathematicians, engineering students, and anyone studying signal processing or harmonic analysis who seeks to understand the convergence properties of Fourier series.
The numbers in parentheses are, respectively, the usual definition of a Fourier series, and the formulas for the coefficients of the series.If a periodic function f(x) with period ##2\pi## is piecewise continuous in the interval ##-\pi \leq x \leq \pi## and has a left-and right-hand derivative at each point of that interval, then the corresponding Fourier series (7) [with coefficients (6)] is convergent. Its sum is f(x), except at a point x0 at which f(x) is discontinuous and the sum of the series is the average of the left- and right-hand limits of f(x) at x0.
robertjford80 said:
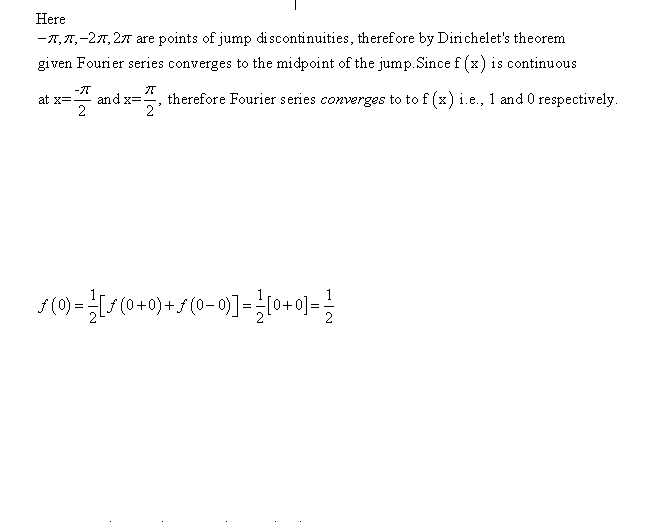
The Attempt at a Solution
Obviously brackets mean something other than parentheses because .5[0 + 0] ≠ .5