- #1
Bruno Tolentino
- 97
- 0
I was reading about double integral when a doubt came to my mind: how to find the antiderivative of the function f(x,y), like bellow, and compute the fundamental theorem of calculus for double integral?
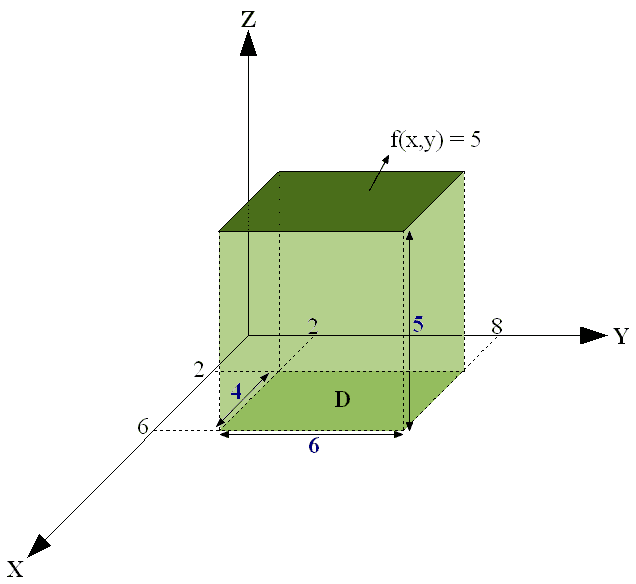
[tex] \int_{2}^{8} \int_{2}^{6} f(x,y) dx \wedge dy = ?[/tex]
OBS: It's not an exercise. I know how to compute the integral above, but, I don't know how do it through of the antiderivative and applying the theorema fundamental of calclus, like that [tex] \int_{a}^{b} f(x) dx = \int_{a}^{b} \frac{dF(x)}{dx} dx = F(b) - F(a)[/tex]. I'm not found anything similar to this...
[tex] \int_{2}^{8} \int_{2}^{6} f(x,y) dx \wedge dy = ?[/tex]
OBS: It's not an exercise. I know how to compute the integral above, but, I don't know how do it through of the antiderivative and applying the theorema fundamental of calclus, like that [tex] \int_{a}^{b} f(x) dx = \int_{a}^{b} \frac{dF(x)}{dx} dx = F(b) - F(a)[/tex]. I'm not found anything similar to this...
Last edited: