SUMMARY
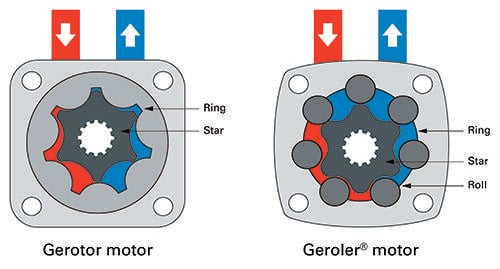
This discussion focuses on calculating the displacement and torque of a custom Geroler motor for a hobby project. Key calculations involve determining the areas opposing input and output pressures, the crank radius, and the differential fluid pressure. The torque formula is defined as T = R * 2 * dP * A, where A is the face area of the gear teeth. The conversation also highlights the advantages of using rollers over traditional gears to reduce friction and wear.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Geroler motor mechanics
- Familiarity with torque calculations and fluid dynamics
- Knowledge of CAD software for design and area calculations
- Basic principles of pressure differentials in fluid systems
NEXT STEPS
- Research Geroler motor design principles and specifications
- Learn about CAD software capabilities for calculating areas
- Study fluid dynamics, particularly in compressible fluids like air
- Explore the differences between Geroler and Gerotor motors
USEFUL FOR
Engineers, hobbyists, and designers interested in custom motor design, particularly those focused on optimizing torque and efficiency in fluid-driven systems.