andrevdh
- 2,126
- 116
For some measurements the case gets connected to earth. This somewhat screens the
electroscope from external effects and makes it a more relaible measuring device, otherwise
charges on nearby objects, for instance you, or nearby metallic objects, a lab stand, can influence
its deflection. This changes the electroscope into a capacitor with a somewhat constant
capacitance and makes it suitable for voltage measurements.

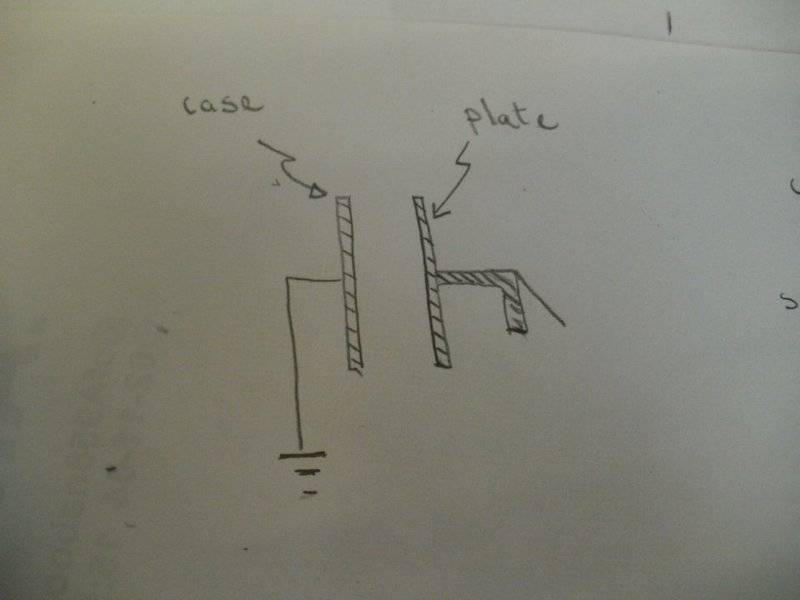
The electroscope is also used without earthing the case. As you know it can be charge by induction.
That is charging the electroscope without bringing the charged object into direct contact with the plate
or cap. In this instance the plate is earthed momentarily while holding the charged rod nearby. We then
get that the rod pulls the opposite charge from Earth onto the electroscope. The Earth is then removed
and finally the rod, leaving the electroscope with a charge opposite to that of the rod.
electroscope from external effects and makes it a more relaible measuring device, otherwise
charges on nearby objects, for instance you, or nearby metallic objects, a lab stand, can influence
its deflection. This changes the electroscope into a capacitor with a somewhat constant
capacitance and makes it suitable for voltage measurements.
The electroscope is also used without earthing the case. As you know it can be charge by induction.
That is charging the electroscope without bringing the charged object into direct contact with the plate
or cap. In this instance the plate is earthed momentarily while holding the charged rod nearby. We then
get that the rod pulls the opposite charge from Earth onto the electroscope. The Earth is then removed
and finally the rod, leaving the electroscope with a charge opposite to that of the rod.
Last edited: