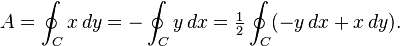SUMMARY
Green's Theorem provides a method for calculating the area of a region enclosed by a curve using line integrals. Specifically, when defining the vector field as ##\vec F = \langle P(x,y), Q(x,y) \rangle##, the choices of M = x and L = -y are valid because they yield the condition ##Q_x - P_y = 1##, which simplifies the double integral to represent the area. The theorem allows for arbitrary choices of P and Q, as long as they satisfy this condition. This flexibility is crucial for various applications in vector calculus.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of vector fields and line integrals
- Familiarity with double integrals in multivariable calculus
- Knowledge of Green's Theorem and its applications
- Basic proficiency in calculus notation and operations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of Green's Theorem in detail
- Explore alternative choices for P and Q in Green's Theorem
- Learn about applications of Green's Theorem in physics and engineering
- Investigate related theorems such as Stokes' Theorem and the Divergence Theorem
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in mathematics, physics, and engineering who are looking to deepen their understanding of vector calculus and area calculations using Green's Theorem.