silin
- 26
- 0
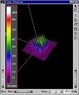
Does anybody know what can be the reason for such an aberration of initially Gaussian shaped laser beam (see attached picture)? Optical elements in the light path: linearly polarized diode 470nm laser, single mode polarization conserving fiber, collimator, mirror, lens, round 50 micrometer pinhole, lens, filter for 470nm line, dichroic beam splitter reflecting 470nm light, mirror, Olympus IX70 microscope. The picture is the beam profile after the tube lens in the microscope. I have already checked all elemets for causing this aberration by removing them one by one, the problem with this lattice like beam shape becomes really pronounced when I leave both lenses in the optical path, but it loos really strange, as if some kind of diffraction pattern. If somebody has any idea please tell, it´s pretty urgent.