Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the behavior of capacitors in a circuit, specifically focusing on the voltage across capacitors after a switch is closed. Participants explore concepts related to charge conservation, energy loss, and the impact of resistance in the circuit over time.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
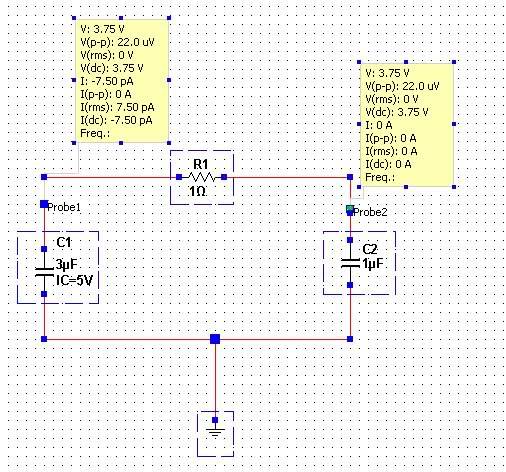
- One participant expresses confusion about why the voltage across both capacitors is 3.75V after the switch is closed, given that the initial charge on one capacitor was 5V.
- Another participant questions whether the voltage measurements are taken at the initial time or at a later time, suggesting the addition of a switch to the schematic for clarity.
- A different participant notes that the presence of a resistor implies that the voltage will eventually decay to zero, regardless of the initial conditions.
- One participant clarifies that they are measuring the voltage at 60 seconds after the switch is closed and reiterates the observed voltage of 3.75V on both capacitors.
- Another participant explains that the charge on the first capacitor is conserved when the switch is closed, leading to a voltage drop due to the combined capacitance of the capacitors in parallel.
- One participant calculates the initial and final stored energy in the circuit, noting a loss of energy due to resistance when the switch is closed.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the interpretation of voltage measurements and the implications of resistance in the circuit. There is no consensus on the understanding of the voltage behavior after the switch is closed.
Contextual Notes
Participants reference specific times for measurements and the effects of resistance, but there are unresolved assumptions regarding the circuit's configuration and the timing of the measurements.