SUMMARY
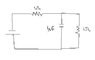
The time constant in an RC circuit is defined as T=RC, but in circuits with multiple resistors, the equivalent resistance must be calculated. For the given circuit with resistors R1 and R2 both equal to 1 ohm, the equivalent resistance R is 0.5 ohm, leading to a time constant of T=RC/2. The voltage across the capacitor can be expressed as v_c(t) = (V/2)(1 - e^(-2t/RC)). Understanding Thevenin's theorem is crucial for analyzing circuits with multiple resistors and capacitors.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of RC circuits and time constants
- Familiarity with Thevenin's theorem
- Basic knowledge of differential equations
- Ability to analyze circuit components in series and parallel
NEXT STEPS
- Study Thevenin's theorem for circuit simplification
- Learn to solve differential equations in circuit analysis
- Explore the behavior of capacitors in charging and discharging scenarios
- Investigate the impact of varying resistor values on time constants
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in analyzing and designing RC circuits will benefit from this discussion.