Discussion Overview
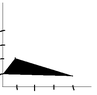
The discussion revolves around the integration of the function \(y^3\) over a triangular region defined by the vertices (0,1), (1,2), and (4,1). Participants explore the setup for a double integral, focusing on determining the appropriate limits of integration and the equations of the triangle's sides.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Mathematical reasoning
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- Some participants express confusion about how to set up the double integral for the triangular region.
- One participant suggests starting the integration at \(y=1\) and describes a method involving horizontal rectangles to find the area.
- Another participant corrects the approach, emphasizing the need for a double integral and providing a formula involving the range of \(x\) as a function of \(y\).
- There is a discussion about finding the equations for the sides of the triangle, particularly side AB, with one participant deriving the equation \(y=x+1\).
- Another participant mentions the need for the equations of both sides AB and BC to establish the limits for \(x\) in the double integral.
- One participant proposes an alternative formulation for the integral, confirming the previous calculations.
- There is uncertainty regarding the equation for side BC, with conflicting claims about its expression, leading to further questioning and reevaluation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the correct equations for the sides of the triangle or the limits of integration. Multiple competing views and uncertainties remain regarding the setup of the double integral.
Contextual Notes
Participants express uncertainty about the equations of the triangle's sides and the correct limits for the double integral. There are unresolved mathematical steps and dependencies on the definitions of the triangle's boundaries.