ynyin
- 3
- 2
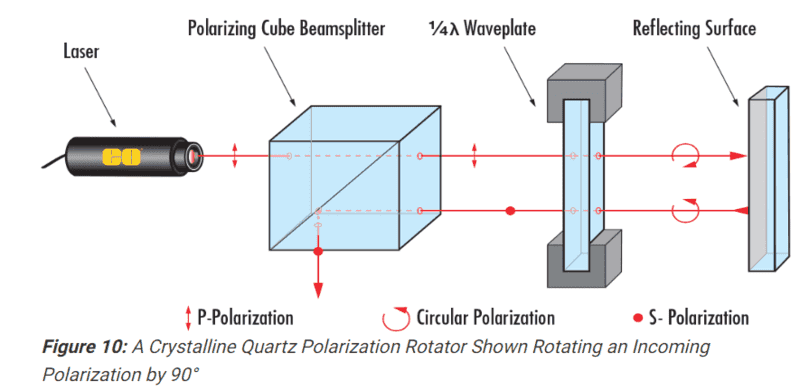
In optics experiments, I often see the following optics configuration to rotate the polarization of an incident linearly-polarized laser beam. The final reflected beam has its polarization rotated by 90 degrees. My question is:
1) Between the quarter plate and the mirror( reflecting surface), the following figure indicates the handness of the circular polarization does not change when it is reflected back. But from what I learned, the polarization should change its handness while being reflected by a mirror. (see, e.g. this question: https://physics.stackexchange.com/q...se-polarization-of-circularly-polarised-light)
2) If the circular polarization changes its handness, then after the quaterplate it should become the same linear polarization as the incident laser beam, meaning that it should pass through the PBS again and not be refleted away.
Where could I be wrong in understanding its principle? Thanks!
1) Between the quarter plate and the mirror( reflecting surface), the following figure indicates the handness of the circular polarization does not change when it is reflected back. But from what I learned, the polarization should change its handness while being reflected by a mirror. (see, e.g. this question: https://physics.stackexchange.com/q...se-polarization-of-circularly-polarised-light)
2) If the circular polarization changes its handness, then after the quaterplate it should become the same linear polarization as the incident laser beam, meaning that it should pass through the PBS again and not be refleted away.
Where could I be wrong in understanding its principle? Thanks!