henry wang
- 30
- 0
How is pi/L part deduced in (n*pi*x)/L?
The constant pi/L in the Fourier series is derived from the requirement that the fundamental frequency is periodic in space with a spatial period of 2L. The relationship is established through the equation ω = π/L, which arises from the periodicity condition cos(ωx) = cos(ω(x + 2L)). This transformation allows the series to be defined over the interval [-L, L] instead of the restricted domain [-π, π]. The normalization factor π is essential due to the periodic nature of sine and cosine functions, which have a period of 2π.
PREREQUISITESMathematicians, physicists, and engineers involved in signal processing, wave mechanics, and any field requiring an understanding of Fourier series and their applications in periodic functions.
henry wang said: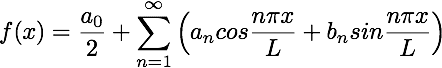
How is pi/L part deduced in (n*pi*x)/L?