SUMMARY
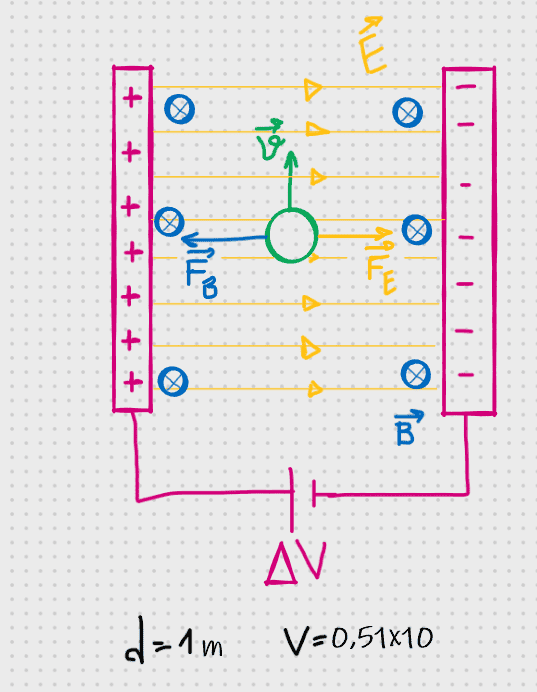
The discussion centers on calculating the power of a voltage supply in the context of a spectrometer's velocity selector region. Participants clarify that the power required to maintain an electric field in isolation is zero, as the energy to create the electric field is drawn from the voltage source. The relevant equation for energy in a capacitor is provided as E = 1/2 CV², where C is the capacitance. The conversation emphasizes the need for clarity regarding the definitions of power and the specifics of the charged particle involved in the problem.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric fields and capacitors
- Familiarity with the concept of power in electrical circuits
- Knowledge of basic physics principles regarding charged particles in magnetic fields
- Ability to interpret equations related to electrical energy and power
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of electric fields and their role in capacitors
- Learn about the relationship between voltage, current, and power in electrical circuits
- Research the dynamics of charged particles in magnetic and electric fields
- Explore the design and function of spectrometers, focusing on the velocity selector region
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics, electrical engineering, and anyone involved in designing or analyzing spectrometers and their components.